Companies require information to make correct business decisions, which in turn, helps them survive the stiff competition. Information pertaining to their business, surroundings, competitors, and impending future – all these enable a business to make a comprehensive strategy to thrive. This whole process of acquiring information to enable intelligent decision-making is termed Business Intelligence (BI). In this article, we will explore the tasks and responsibilities involved in the business intelligence value chain.
What is business intelligence value chain?
Business Intelligence (BI) is a type of architecture that supports collecting and analyzing data to come up with meaningful information about the business. Owing to the competitive environment, companies are heavily investing in data warehousing, analytics, and reporting for informed decision-making. This whole decision-making process comprises a chain of methodologies, and is known as the ‘Business Intelligence Value Chain’.
This system is designed to have a methodological structure to take raw data and generate meaningful insights from them that leverage business value. Over time, this system has evolved to have more concrete and properly defined stages. Leaders can use the BI value chain to form better strategies, processes, structures, and systems to deal with internal and external threats.
5 Stages of BI Value Chain
There are several stages in converting raw data into meaningful information that, in turn, adds value to the business. These stages are typically referred to as the stages of a Business Intelligences Value Chain. These stages are the following-
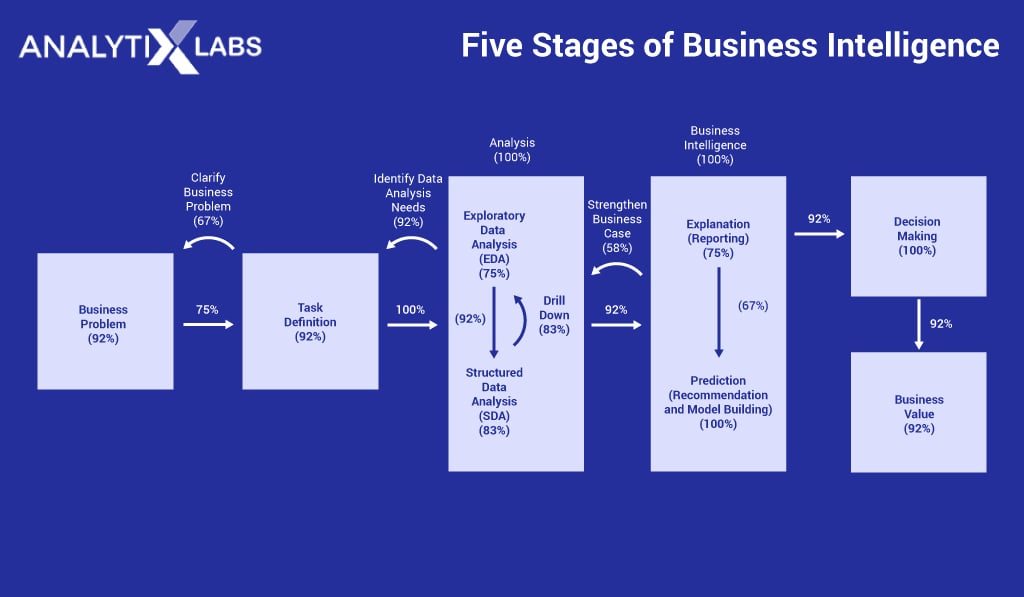
1. Data sourcing
The first step in the BI process is accessing the data. This stage deals with the storage, management, and accessing of raw data. Thus, data warehousing becomes an essential aspect of business intelligence. Sourcing data is of utmost importance as the quality and relevancy of data directly impact the quality of insights gained and the consequent decision taken by the leadership. Another aspect of data sourcing deals with identifying and exploring various data resources. It’s crucial for the following reasons-
- Data can be related to each other
- It can be unstructured (in the form of text, images, or other forms of unstructured data)
- Data can have peculiar features (such as different data types etc.)
It is vital for a business intelligence analyst to know what kind of data is available and where and how they can access it.
2. Data engineering and analysis
After data sourcing, the next logical step is information engineering and analysis. To perform analysis on the data and to gain even the fundamental insights from the data, a BI analyst needs to have the data in a structure that is conducive for analysis. This requires data engineering that includes-
- Converting data into a structured (tabular) format
- Removing or imputing missing values
- Capping outliers
- Removing multicollinearity
Once the data is structured and ready, Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) is performed through which useful information can be synthesized, such as-
- Summarizing data using descriptive statistics
- Finding associations in data
After EDA, Structured Data Analysis (SDA) is performed, which includes three types of analysis-
- Trend Analysis: It’s used for identifying patterns in the data. This includes, for example, assessing sales based on different geographical regions, the volume of product sales over a stipulated period, etc.
- Mathematical Analysis: It’s used for calculating performance and growth using mathematics. This includes, for example, assessing the margin of sales and growth in absolute and in percentage.
- Statistical Analysis: Inferential statistics is used to assess the statistical significance of the patterns and peculiarities being identified in the data. Statistics is also used to perform predictions, analytics, and forecasting using regression and other methods. The statistical coefficients can also be used to perform prescriptive analytics, identifying reasons for certain business phenomena. Therefore, the model building can take place at this stage of Business Intelligence.
To understand how data is analyzed, you must also learn about the univariate analysis of data.
3. Situation awareness
The core of business intelligence is to provide concerned individuals in an organization with knowledge helping in situational awareness. This stage in Business Intelligence deals with report creation and presentations that provide the decision-makers with essential and relevant information to help them be aware of the events in and around the organization. This information can make them aware of, for example, government policies, upcoming market trends, market forces, etc.
4. Decision-making
Once the decision-makers know the ‘what and why’ of the events in and around the business, the next stage is proactive decision-making and its evaluation. The insights, knowledge, and intelligence gained from analytics enable decision-makers to make data-driven decisions. This can be, for example, coming up with strategic decisions such as management change, management of products and categories, opening or shutting of offices, launching of new products, or can be operational, such as promotional campaigns, upsell and cross-sell campaigns, etc.
5. Decision support
This stage deals with supporting the proposed decision by evaluating it. Evaluation includes identifying the risks, opportunities, benefits, profit, pitfalls, cost-to-benefit ratio, return on investment, and estimating the business value of the proposed decisions. All of this helps in making efficient and effective decision-making.
Another way of setting the stages of a Business Intelligence Value chain is to lay them out in terms of complexity. In terms of complexity, the stages are-
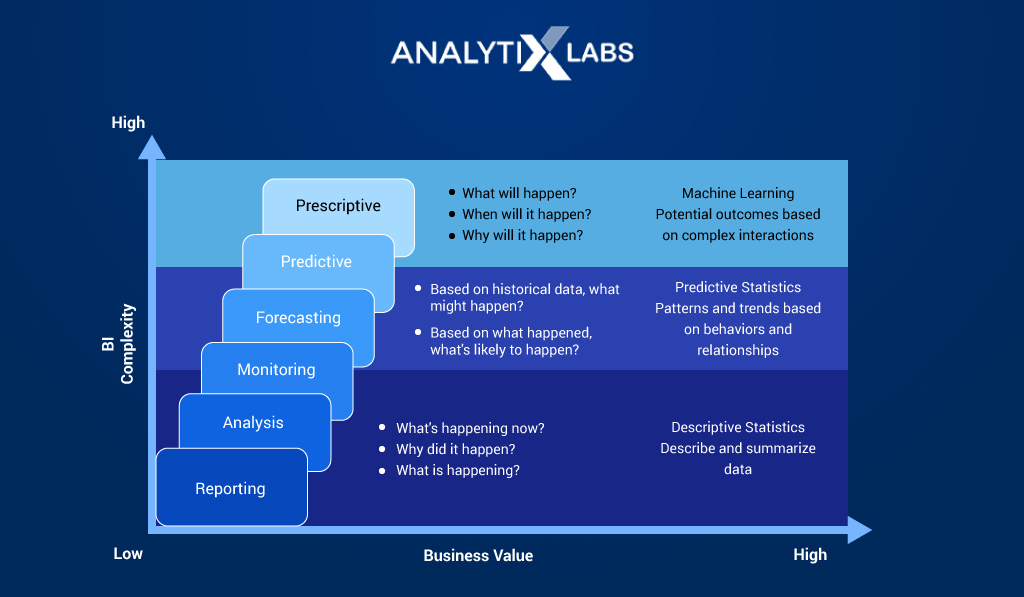
- Reporting: The most basic stage of BI is to understand what is happening and report the same.
- Analysis: The next stage is to answer ‘why did it happen?’ and identify the cause and effect of the events in and around the business.
- Monitoring: This stage deals with answering the question—’ what is happening right now?’ as this deals with keeping an eye on the business’s day-to-day activities.
- Predicting & Forecasting: The next stage is significantly more complex than the previous one as this involves using predictive statistics and even machine learning. Here patterns and trends are assessed through a predictive or forecasting model. This helps answer questions like ‘what will happen given the past data?’
- Prescriptive Modeling: The most complex stage involves prescriptive models to answer questions like ‘What will happen, when will it happen, and why will it happen?”. All this requires understanding complex relationships and interactions between the data features. This stage also deals with re-prediction and re-forecasting to create a feedback loop that helps make models better.
NB: The first three stages use descriptive statistics.
Understanding the value of BI
Business intelligence is essential for any business. Here’s how BI enables a business:
- Cost reduction: The most significant value of Business Intelligence is that it can significantly reduce costs for an organization. This can be achieved by increasing operational efficiency, identifying and eliminating backlogs and delays, performing root cause identification, looking for a solution, and eliminating wasteful resources.
- Increase in revenue: BI’s next significant value addition is helping an organization increase its revenue. Information sharing among leadership and end-users, better market analysis, upskilling the existing workforce, and analyzing customer behavior to design products can help increase revenue.
- Enhancing customer satisfaction: For any business, increasing the satisfaction of its end-user is of paramount importance. While customer satisfaction can be achieved in many ways, BI can help increase customer satisfaction by providing customers with factual information, performing competitive analysis to understand the pros and cons of the product offered by competitors, and analyzing the issues faced by the customers to help in a quick resolution.
Several factors of a business intelligence system influence it and can make or break it. While there are hundreds of factors affecting a business intelligence system, we can group them in the following manner.
Factors influencing the BI system
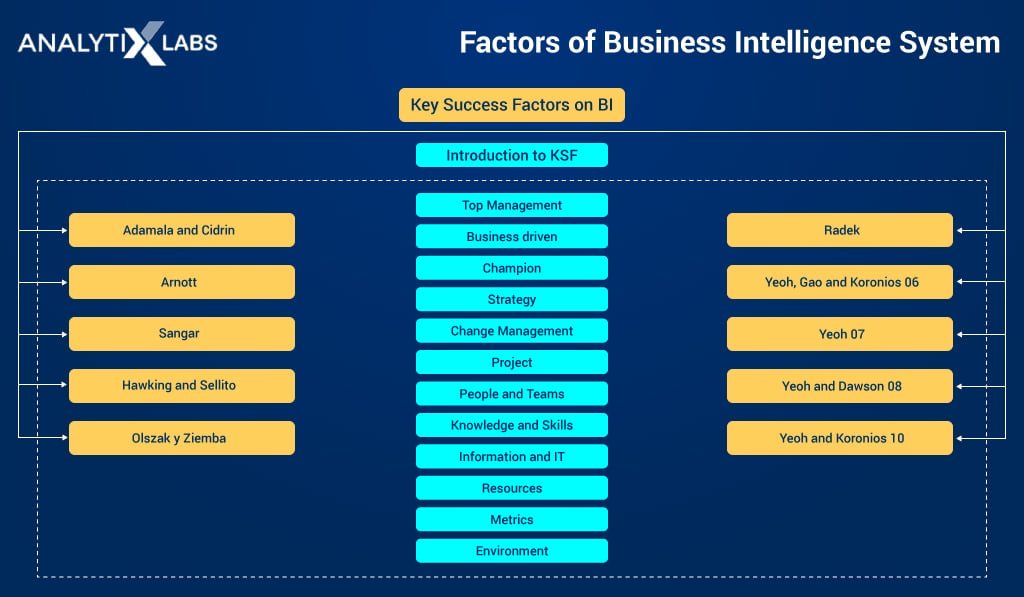
1. Management:
Top management is essential in BI as it provides the directives and necessary support. A team of well-qualified managers is required as their active participation is crucial for the success of any BI project
2. Business Understanding:
Another essential factor of a business intelligence system is how well it links to the business and solves a business problem. A BI project must be well defined, have a straightforward methodology to manage the project, should be managed by the technical as well as the business side, and should have clear goals.
3. Project Manager:
A BI project must be divided into achievable chunks or sub-projects that achieve the larger objective. Each of these projects can have analytical and technical individuals, but the project manager must have an excellent understanding to make sense of the insights provided by the team.
4. Strategy:
An essential factor in a BI project’s success is clear business vision and planning. This can be achieved by spending extensive time creating the strategic framework.
5. Change in Management:
The high-level leadership must be flexible with the team managing the BI project. If the need arises to change the management, it must be done.
6. Project Monitoring:
The project performance must to monitored regularly. The solution provided should be as per the requirement of the end-user, and the project should be flexible as per the changing requirement of the end-user.
7. Human Talent:
The teams involved in the BI project, from the BI project manager to all the team members, should be competent with a clear understanding of the business link and goal. A good balance and mix of skill sets in the team can considerably improve the performance
8. Learning & Upskilling:
Given the dynamic nature of technology, the resources must be upskilled in the newest BI tools and methodologies.
9. Environment:
The environment in which BI analysts and related individuals work should be such that respective people solve technical and non-technical issues on time.
10. Scalability:
The BI products developed in the project must be modular as this help in scalability.
Business Intelligence Lifecycle
A business intelligence life cycle is comprised of several steps.
Few BI lifecycle steps coincide with the 5 stages of BI value chain as well.
A typical business intelligence life cycle has the following steps-
1. Identifying business process and problem
The first step in a business intelligence life cycle is to identify the business problem that BI will aim to solve. This involves understanding the business process, identifying where it is lacking, and the problem being raised from there. For example, the business process of acquiring a new customer through digital marketing can have the issue of budget constraints, causing a lack of new acquisitions. Thus, the problem becomes a lack of new customers, and the question that BI needs to solve now is “How to get new customers efficiently”.
2. Data collection
The next step is to look for data. Continuing the above example, a BI analyst has to look for relevant data that explain how much money was spent on different streams of marketing, the number of customers acquired from each stream, the performance of customers belonging to different streams, customer complaints, and behavior, purchasing history, etc. All this data can be available at various places in different forms. You can use data collection methods to compile important data easily.
3. Data warehousing
Another significant aspect of a business intelligence life cycle is data warehousing. This step involves saving relevant data in RDBMS and other types of database management systems.
4. Data preparation and analytics
The fourth step is to prepare the data stored in a warehouse to perform analytics. This includes monitoring daily activities, coming up with summary stats, and different models such as predictive, prescriptive, forecasting, etc.
5. Reporting
Reporting involves converting the insights gained from analytics into visual friendly and ‘digestible’ forms of reports, dashboards, KPIs, and presentations provided to the decision-makers.
6. Business decision
Based on the reports, the leadership takes strategic and operational decisions. As data back this decision-making, it has a high probability of successfully achieving its objectives. For example, a report can explain the daily acquisition of customers from different marketing streams, the statistical impact of marketing campaigns on acquisitions, and the prediction of the acquisition’s magnitude given a revised amount for marketing. Based on the report, the leadership may decide to cut the funding for digital marketing through Facebook and reallocate the money to Instagram.
7. Evaluation and iteration
The last step is to assess the feasibility of the decision in monetary or even social terms. Once the decision is implemented, it’s essential to check if the decision was successful and to what extent. This feedback is critical as specific tweaks can be made in the decision to make it more effective, thus making the process iterative.
Now let’s take a look at how BI functions in logistics and transportation.
BI in Logistics and Transportation
Organizations across all domains understand the value of BI- from finance to NGOs. However, over the last few decades, the significance of business intelligence in logistics & transportation has drastically changed this industry for good. Today, many companies outsource their logistic work to thirds party logistics providers (3PLP). These companies have heavily involved business intelligence in their work and have resulted in performance improvement of their services. However, BI also helps streamline the organizational and IT aspects of such companies.
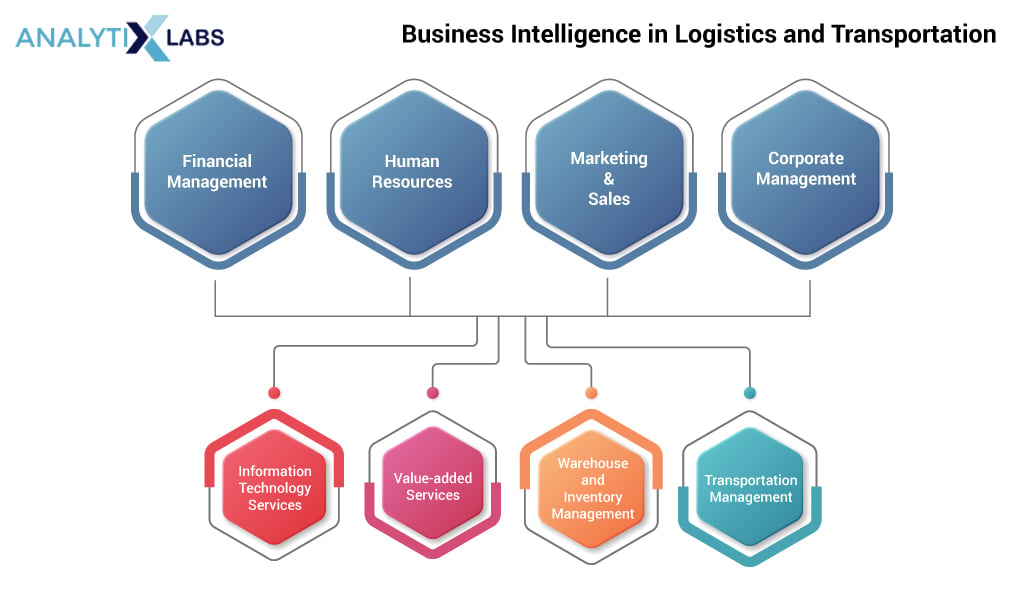
The BI value is evident in the services by 3PLP. Through detailed monitoring of the daily working and in-depth analytical reports on the functioning of these services, these companies have made it possible to improve and become profitable.
Transportation Management
BI helps in route optimization, traffic control, efficient selection of mode of transportation, etc. Various types of analysis are performed here, such as
- Carrier performance evaluation to select the best third-party carrier
- Analysis of the performance of truck drivers to maximize performance with safety
- Capacity analysis to better manage the resources and minimize loss of revenue by planning capacity in advance
- Analysis of supplier compliance to find leakages in payments and reduce delays
- Scheduling root that takes minimum time and fuel
- Analysis of mode-cost to identify the best mode of transportation for different products
Warehouse & Inventory Management
Many logistics companies store produce they transport, and managing the warehouse becomes essential. Here BI helps in-
- Analysis of inventory to understand the currently available products and their associated information (shape, size, and shelf life).
- Analysis of the performance of warehouses by creating KPIs (such as on-time shipments, time taken to pick up products from warehouses, etc.)
- Analysis of warehouse costs by analyzing the dimensions and handling requirements of the products stored there.
- Analysis of products picked from warehouses to efficiently group products and place them around each other during storage
- Analysis of warehouse space utilization to better understand how the space is being utilized to use it efficiently
Value Added Service
3PLP also provides other services such as handling reverse logistics, packing, labeling, assembly, etc. These value-added services are the ones that often make companies stand out. However, business intelligence in logistics is used to identify the cost-benefit analysis of these services and analyze each of these services to manage their workings efficiently.
As mentioned earlier, BI not only helps the logistics companies make their services better but also helps provide organizational and IT support. For example, BI provides organizational support through better financial, human resources, marketing, sales, and corporate management. On the other hand, BI delivers IT support to such companies by improving supply chain visibility, performing forecasting, and customer reports. Going into the details of all such aspects is beyond the scope of this article, but you certainly can explore them.
Below are a few commonly asked questions on the Business intelligence value chain. If you have more queries, drop in the comment section or reach out to us directly.
Business Intelligence Value Chain: FAQs
- What are the five stages of business intelligence?
The five stages of business intelligence are Data Sourcing, Data Engineering & Analysis, Situation Awareness, Decision Making, and Decision Support. In terms of complexity, it can be Reporting, Analysis, Monitoring, Predicting & Forecasting, and Predictive Modeling.
- What is the last step of the business intelligence value chain?
The last step in a business intelligence value chain is to evaluate the decision made by the leadership. This includes considering their decision’s ROI, risk, and business value and eventually monitoring how well the decision performed. The step extends to identifying the reasons for the success/failures of the decision and iterating over it to make it better.
- How does business intelligence provide business value?
Business Intelligence enables intelligent decision-making that is backed by data. This reduces the chance of making the wrong decision based merely on ‘intuition’ or ‘gut feeling’. The eventual result is efficient and effective decision making, eventually helping increase profit, reducing cost, and staying up to date.
The increased demand for skilled business intelligence analysts shows how important BI is for any organization of any size. While a handful of institutes provide industry-relevant training in the data science domain, AnalytixLabs is one of the premium institutes in India that offer specialized courses on BI. So, if you want to leverage the increasing scope in the BI field, start your learning now.
Aiming to start your career in BA? You can join our course in business analytics and learn all the fundamentals and advanced aspects at your convenience, or you can book a demo with us.
Additional resources you can read:









2 Comments
Archish, you’ve written a fascinating post!
Cost reduction and increased revenue are critical goals for any business, and BI seems to be a powerful tool in achieving them. The concept of using data-driven insights to identify and eliminate inefficiencies is intriguing. Are there any specific examples of companies that have successfully implemented BI for cost reduction, and what were the outcomes?