Market Mix Modeling uses marketing mix techniques and software to determine the effectiveness and ROI of a company’s marketing strategy. The analysis can help identify where resources are wasted, which tactics drive the most results, and how changes to the current strategy could improve performance.
It combines data from multiple sources, such as market research, surveys, financial reports, internal data, etc., with a mathematical model to predict outcomes for various marketing strategies.
As the modern marketing landscape becomes increasingly complex, IT students and professionals, aspiring data engineers, developers, and data engineers need a deep understanding of the role of Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM) in the marketing world.
This article will introduce MMM, explain how it works, and discuss its advantages and limitations. We will also look at some real-world case studies and delve into techniques used to implement these models.
What is Market Mix Modeling?
Marketing Mix Modeling is an analytical approach used to quantify the impact of various marketing tactics on sales performance, profitability, and return on investment (ROI). It assists marketers in making data-driven decisions, optimizing their marketing mix, and allocating their budget across channels and tactics to achieve their desired goals.
Elements of a Market Mix Model (MMM Marketing)

- Price refers to the amount consumers are expected to pay for a product or service. It is one of the most important variables in the marketing mix and can impact sales volume, market share, customer loyalty, profitability, etc. Companies need to consider their target customers when setting prices so they don’t overprice and lose potential buyers.
- Place refers to where products and services are sold. It includes physical locations like stores and online platforms that allow people to purchase goods remotely. Companies looking to maximize their reach and visibility among potential customers must understand traditional and digital distribution channels.
- People refer to the individuals who interact with a brand, from customer service staff to sales representatives. Companies must ensure that their employees represent the company’s values and know about the products and services they sell.
- Product refers to the goods and services offered by a business. Companies need to understand what features customers want so they can create products or services that meet those needs. Good product design can be important in achieving a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
- Process refers to how a product or service is delivered to customers. A well-designed process ensures that customers receive their orders quickly, accurately, and with minimal effort. Streamlining processes can also help save time and money for businesses.
- Promotion involves communicating with customers about the products and services a company offers. It includes advertising, public relations, promotions, etc. Companies must understand their target audience and tailor their communication accordingly to get the most out of promotional campaigns.
Marketing Mix Modeling allows marketers to determine which marketing mix elements impact their sales and ROI most.
By using Marketing Mix Modeling, companies can understand their customer base better and make more informed decisions about their future plans. It can help analyze past performance, identify trends and correlations between marketing tactics, and forecast future results. Companies can pinpoint areas of improvement.
Additionally, it helps marketers make informed decisions regarding budget allocations across channels and tactics and optimize communication strategies over time.
How Does a Marketing Mix Model Work?
MMM marketing uses historical data on marketing expenditures, sales performance, external factors (such as seasonal trends and competitive activities), and other relevant variables.
It creates a regression model that estimates the contribution of each marketing tactic to sales revenue while considering the influence of non-marketing factors.
This effectively predicts the changes in marketing efforts that will likely impact sales and make adjustments to enhance campaign performance and ROI.
For example, marketers can decide where to invest their budget. This can be done by understanding how much of a sales increase should be attributed to an increase in email marketing spend versus search advertising or other tactics.
Additionally, MMM can be used for long-term campaigns such as product launches and annual advertising initiatives. By using historical data and analyzing trends in the market over several years, marketers can plan their budgets, set realistic expectations for each tactic’s performance, and develop impactful MMM models.
The outcome of a marketing mix model is often presented in the form of contribution charts. These charts show the incremental effect of each campaign element on sales. These charts are useful for illustrating which elements contribute most to ROI and informing future decision-making.
What is a Contribution Chart?
A contribution chart visually represents different marketing tactics’ impact on sales. It shows how much each tactic contributes to the total sales and highlights the most effective ones.
The chart can be used to benchmark performance, compare campaigns over time, and plan for future initiatives. Contribution charts provide an easy-to-understand overview of where a marketer’s efforts should be focused to maximize ROI and optimize campaign performance.
There are two types of contribution charts:
- Absolute contributions summing up to 100%
- Non-absolute contributions summing up to 100%
Let’s understand what these mean.
-
Absolute contributions summing up to 100%
It shows exactly how much each tactic contributes to total sales. It is useful for identifying which tactics have the most significant effects on revenue and examining changes in contributions over time. It allows marketers to see if certain tactics perform better than others and adjust their strategy accordingly.
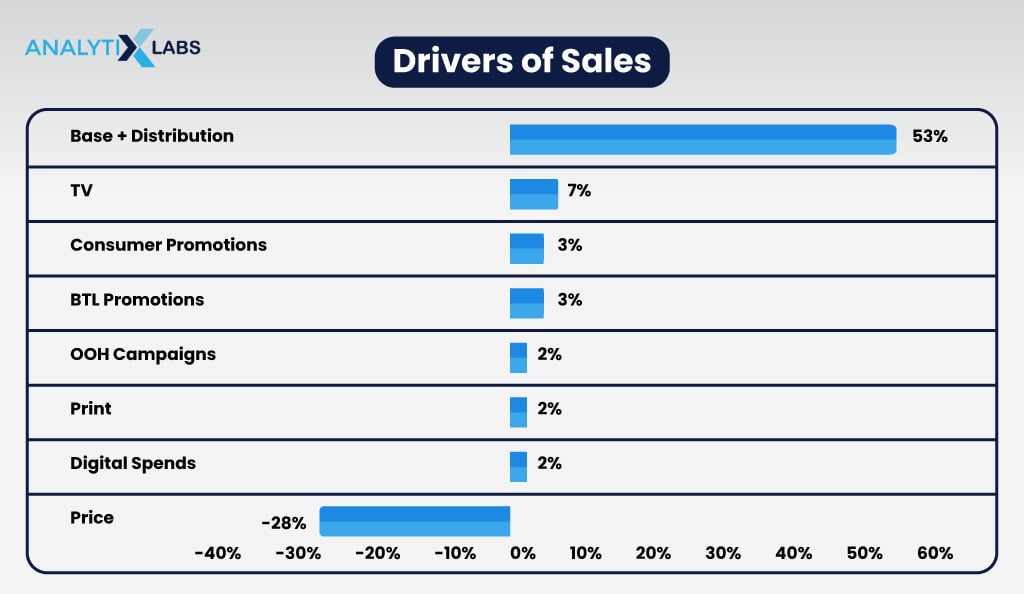
-
Non-absolute contributions summing up to 100%
Non-absolute contribution charts show the relative importance of each tactic in terms of its contribution toward total sales. The information can help marketers understand which tactics may not be as effective as others, allowing them to adjust their budgets accordingly.
Additionally, non-absolute contribution charts can be useful for comparing different campaigns or initiatives as it makes it easier to see which tactics in each campaign had the most significant impact on sales.
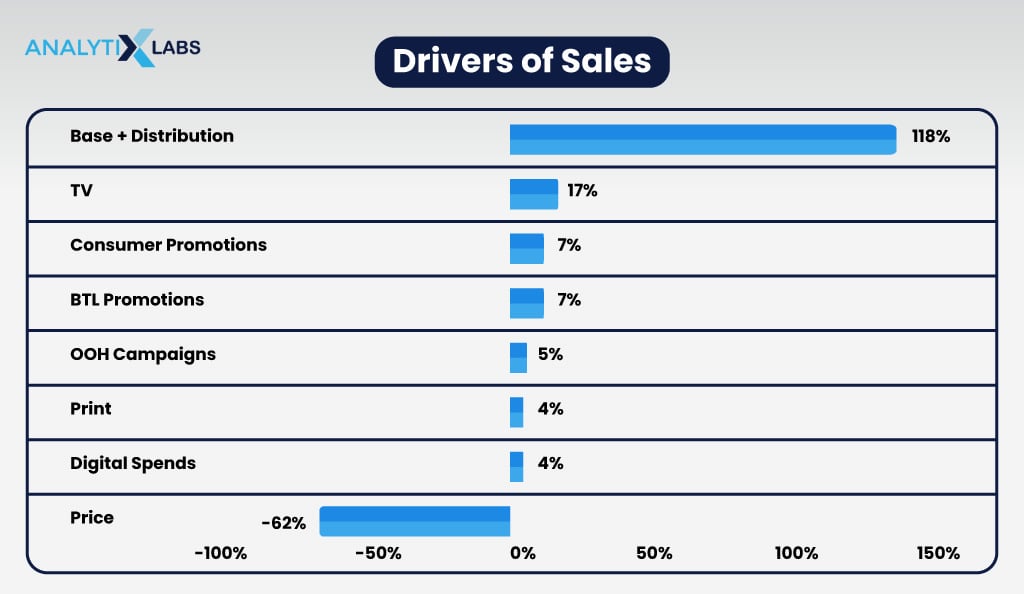
Visualization of data using contribution charts can help marketers make decisions quickly and easily understand the impact of their campaigns at a glance.
With this knowledge, they can adjust their strategy accordingly and ensure that their budget is allocated in the best way possible.
Additionally, contribution charts enable more strategic planning by helping marketers understand which tactics contribute the most to sales and where to allocate the budget for future campaigns.
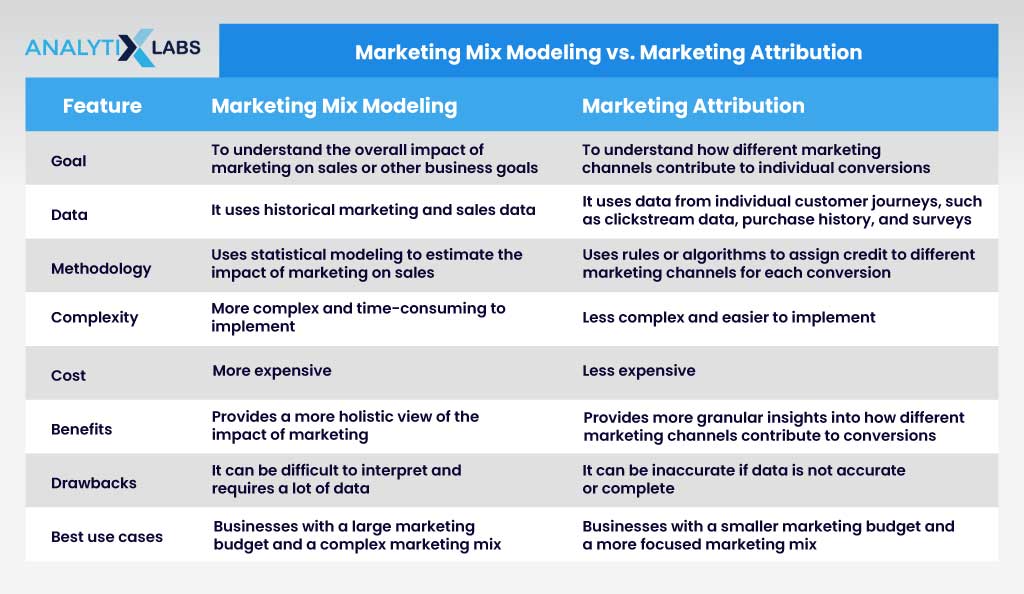
Market Mix Modeling vs. Market Attribution
While MMM marketing and marketing attribution aims to measure marketing activities’ effectiveness, their focus and methodology differ.
MMM models analyze the impact of marketing activities at a more macro level, considering how different channels and tactics work together to drive business outcomes. On the other hand, marketing attribution operates on a more granular level, assigning credit to specific customer touchpoints along the conversion path.
Both approaches have their strengths, and a comprehensive approach to marketing measurement may involve using both MMM and attribution to derive actionable insights.
How to Get Started with Marketing Mix Models?
Marketing mix modeling uses multi-linear regression (MLR) to determine the impact of different elements of a company’s marketing plan on sales or other desired outcomes.
The model examines product placement, advertising campaigns, promotions, and pricing strategies over time. It provides insights into what activities have impacted past performance and which variables should be adjusted for future success.
MLR requires you to define the dependent and independent variables. The dependent variable is the outcome to be measured, like the volume of sales, revenue, or market share.
The independent variables represent elements of the marketing mix believed to influence performance, such as advertising spend, pricing, promotion, and distribution.
Getting started with marketing mix modeling (MMM) involves the following simple steps:

- Gather data: Compile historical data about your marketing activities and associated costs like advertising spend, website visits, customer loyalty program memberships, and more. You will also want to collect sales data for the products or services being marketed to evaluate the effectiveness of each campaign or channel.
- Select variables: Choose the marketing channels and tactics you want to analyze, along with relevant control variables like seasonality, competitor activity, and economic factors.
- Develop the model: Create a mathematical model that considers all the variables. Using statistical techniques like linear regression, estimate the relationship between your marketing mix and sales performance.
- Validate the model: Run different scenarios and test various hypotheses to determine the optimal mix of marketing channels for maximum return on investment (ROI). Look at both short-term and long-term effects and ROI in terms of customer acquisition costs or brand awareness. Use this information to inform future decisions and investments.
- Optimize the marketing mix: Make adjustments based on the model’s insights and track outcomes over time to optimize your marketing mix. It could include changing allocations between different channels or introducing a new type of marketing activity.
- Measure success: Evaluate the results of your efforts and use this information to inform future strategies. Focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales growth, customer acquisition costs, revenue per customer, and lifetime value (LTV).
Marketing Mix Modeling Techniques
There are several techniques used to implement Marketing Mix Modeling (MMM):
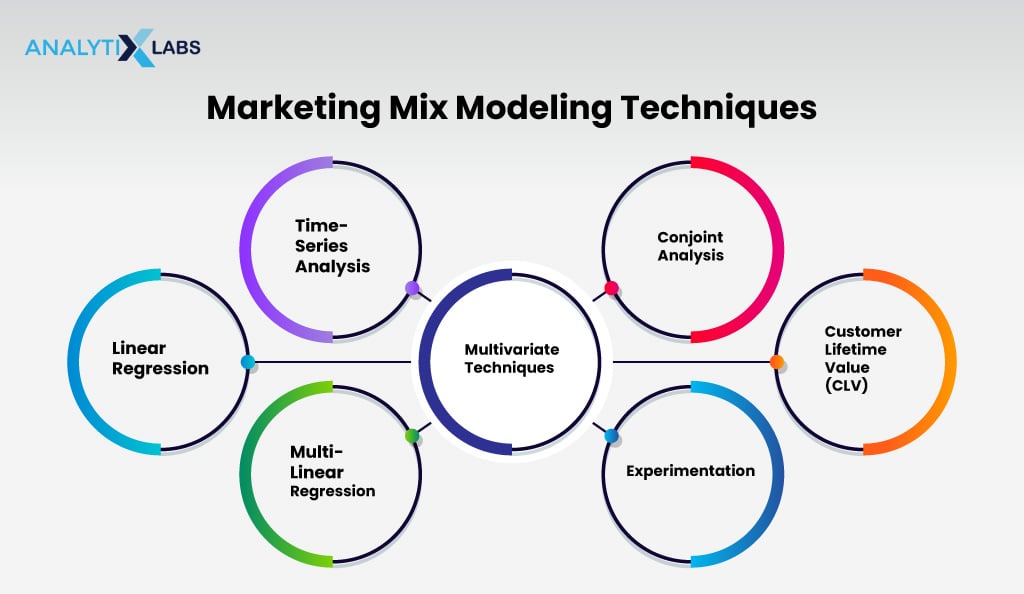
-
Linear regression
Linear Regression is the most common method, where marketing channels and tactics are modeled as independent variables, and sales performance is the dependent variable. It involves a series of mathematical calculations that will result in an equation that describes a line that best fits the data points.
-
Time series analysis
The time-series analysis technique involves analyzing sales performance over time to explore trends, seasonality, and the relationship between marketing activities and sales. When analyzing time-series data, four components should be examined:
- Secular trend: A long-term pattern of slow or steady growth or decline that often occurs over a period of several years.
- Seasonal variations: These occur annually, such as in the case of holiday sales.
- Cyclical fluctuations: These are recurring patterns that tend to recur at regular intervals (generally measured in terms of years).
- Irregular variations: These include unpredictable short-term changes that cannot be attributed to any other factor.
-
Multi-linear regresion
The approach uses statistical models to identify the impact of marketing activities on desired outcomes. It involves collecting data from different sources and applying regression analysis to identify relationships between variables such as sales, cost, and media activity.
-
Multivariate techniques
Multivariate techniques are used in market mix modeling to uncover relationships between marketing activities and performance outcomes. It includes factor and principal components analysis that help identify underlying patterns and relationships among marketing variables.
Also read: How Univariate Analysis helps in understanding data
-
Experimentation
MMM can also test different marketing strategies through experimentation with controlled campaigns. A/B testing is a popular method for this purpose, where two versions of an advertisement are tested against each other to determine which one performs better in terms of customer engagement or return on investment (ROI).
-
Conjoint analysis
The conjoint analysis technique evaluates how customers weigh various product attributes when purchasing. It involves asking survey respondents questions that allow them to make trade-offs between different products. The data can then be used to inform product decisions and marketing campaigns.
-
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
CLV approach measures the total revenue a company will receive from a customer over their entire journey. It is useful for understanding customer behavior regarding loyalty, engagement, or response to marketing messages.
Also read:
These techniques are just some of the many ways marketers can use MMM to improve decision-making around budget allocation, media mix, and other key strategic areas.
By gathering insights into how customers respond to various touchpoints and channels, companies can ensure they target the right audience with the most effective message at the optimal time. It ultimately leads to stronger ROI on marketing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Market Mix Modeling
Advantages:
- Data-driven decision-making: MMM helps businesses make more informed decisions based on quantitative evidence, reducing reliance on intuition or gut feelings.
- Optimized marketing budgets: MMM allows marketers to better allocate their budgets across channels and tactics with the most significant impact.
- Improved ROI: By investing in high-performing marketing activities, businesses can expect an improved return on their marketing investments.
- Better execution of marketing campaigns: MMM helps marketers identify and prioritize the most effective marketing strategies and tactics, leading to more successful campaigns.
- Increased customer lifetime value: By understanding customer behavior across channels, businesses can better target their campaigns and increase customer lifetime value (CLTV).
- Enhanced targeting efforts: With a deeper understanding of how different groups respond to targeted messages, businesses can customize their messages for maximum impact.
- Testing business scenario: MMM allows businesses to test and compare different business scenarios, enabling them to make more informed decisions in the long term.
- Analyzing marketing effectiveness: With a holistic view of how their campaigns are performing, marketers can better understand what’s working and what is not, allowing them to adjust their strategies accordingly.
- Improved customer experience: With access to detailed customer insights, businesses can tailor their offerings based on individual preferences, leading to higher satisfaction levels among customers.
Limitations:
- Data quality: Poor data quality or incomplete datasets can lead to inaccurate results.
- Model complexity: As models become more complex, they require more resources and expertise to develop and maintain.
- External factors: Since MMM relies on historical data, external changes or competitors’ actions may invalidate assumptions made in the model and reduce its accuracy.
- Cost: Marketing mix modeling is relatively expensive to implement and maintain. It also requires dedicated staff and resources to develop, interpret, and act on the results.
- Time lag: Due to its reliance on past data, MMM may not provide an accurate prediction of what the future holds. The longer the time lag between when a decision is made and when it is implemented, the less accurate the model will be.
- Granularity: In order to provide more detailed insights, MMM models must often take into account multiple layers of granular data points, which can require advanced analytics capabilities that are cost-prohibitive for some organizations.
Conclusion
Marketing Mix Modeling is a powerful tool for data engineers, marketing professionals, and IT students to gain insight into a company’s marketing activities and optimize their campaigns for maximum ROI.
By understanding the advantages and limitations of MMM, marketers can make data-driven decisions that drive growth and profitability for their businesses.
FAQs
-
What is an example of marketing mix modeling?
An example of marketing mix modeling is a marketer who wants to determine how effective their various marketing channels are at driving sales. The marketer would use a marketing mix model to analyze data from different marketing channels, such as website traffic, email campaigns, social media ads, and traditional advertising.
You can determine which channels generate the most sales for the least cost. By understanding these channels and how each contributes to sales, the marketer can adjust strategies and budgets accordingly. The analysis helps marketers optimize their investments in different marketing channels to maximize their return on investment (ROI).
-
How to create a market mix model?
Creating a market mix model is important for understanding the impact of various marketing strategies on sales, volume, and profit.
It involves the following steps:
- Identify the relevant factors that need to be analyzed, like demographics, seasonality, pricing strategies, promotional campaigns, and customer loyalty programs.
- Gather data from past marketing activities or industry research.
- Build the model based on the gathered data and create a mathematical model that reflects your product or service’s marketplace.
- Test various scenarios and refine your model by changing the mathematical equations based on the scenario analysis.
- Present results to stakeholders so they can make informed decisions about their marketing investments.
-
What are the 4 Ps of marketing mix modeling?
The 4 Ps of marketing mix modeling is a set of key elements used to assess the success and return on investment (ROI) of marketing campaigns. These include:
- Product- It refers to the goods or services being offered by a business. It includes features such as design, packaging, quality, support services, warranties, and product range.
- Price- The amount customers pay for products and services. Pricing strategies involve setting prices based on customer demand and the perceived value of the product or service.
- Promotion- It encompasses all activities related to advertising a product or service to create awareness about the product or service through various channels like television ads, radio commercials, and online campaigns.
- Place- It refers to the channels used by a business for the distribution of its products and services, including retail stores, websites, or through other third-party distributors.
-
What is the purpose of marketing mix modeling?
Marketing mix modeling is a statistical technique used to analyze past marketing performance in order to predict future results. It helps marketers identify which marketing tactics have had the greatest impact on sales, and optimize their budget spend across channels for maximum ROI.
Beyond optimizing budgets, MMM provides vital insights into customer behavior and preferences. It helps create more consistent messaging and boost long-term growth potential.








