Cloud deployment is a powerful technology that has revolutionized the way businesses operate. From cost savings to increased scalability, Cloud deployment offers extensive benefits for organizations of all sizes.
Cloud computing provides shared resources, software, and information on demand. It lets businesses access applications, storage, and other services from remote servers instead of maintaining their physical infrastructure.
Cloud deployments are highly secure and reliable with advanced security measures such as two-factor authentication. It ensures user data is secured in transit between the user’s device and the Cloud service provider.
A Cloud service enables you to scale your business easily and at lower costs than traditional IT solutions such as on-premise software. This article will give you an overview of what Cloud deployment is and the types of Cloud deployment. We will also discuss the benefits and risks of Cloud deployment and guide you in choosing the right deployment model.
What is Cloud Deployment?
Cloud deployment is when an application or software platform is available to users online. It requires that applications and platforms be hosted on remote servers, allowing them to be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection.
In the past, hosting applications required renting or building data centers to house the servers’ hardware. But, with Cloud deployment, organizations can reduce their hardware costs while still providing access to resources for their employees.
Cloud computing is utilizing computing resources on demand without directly controlling them. So, instead of creating data centers and purchasing hardware to operate apps, organizations can rent computing power and utilize it as needed.
Cloud deployment entails designing, organizing, executing, and running Cloud workloads. Cloud deployment makes different computing environments possible depending on the precise configuration of characteristics, such as ownership and accessibility of the deployment infrastructure.
The biggest benefit of utilizing the Cloud is that users pay for their storage space and electricity. They do not have to bear the expense of running an entire data center. It is also easily scalable based on demand.
Types of Cloud Deployment Models
Cloud Computing involves sharing servers, data storage, and application software. As a result, you only need to request extra resources, and the Cloud makes system setup and operations quicker and easier. Moreover, you only have to pay for the resources you actually use.
The virtualized computing environment can be selected based on the amount of data to be processed and the number of users who need access to the infrastructure.
Cloud deployment models assist in deploying computing resources, such as infrastructure, software, and data storage, over the internet. The following main types of Cloud deployment models are based on Cloud size, capabilities, and ownership.
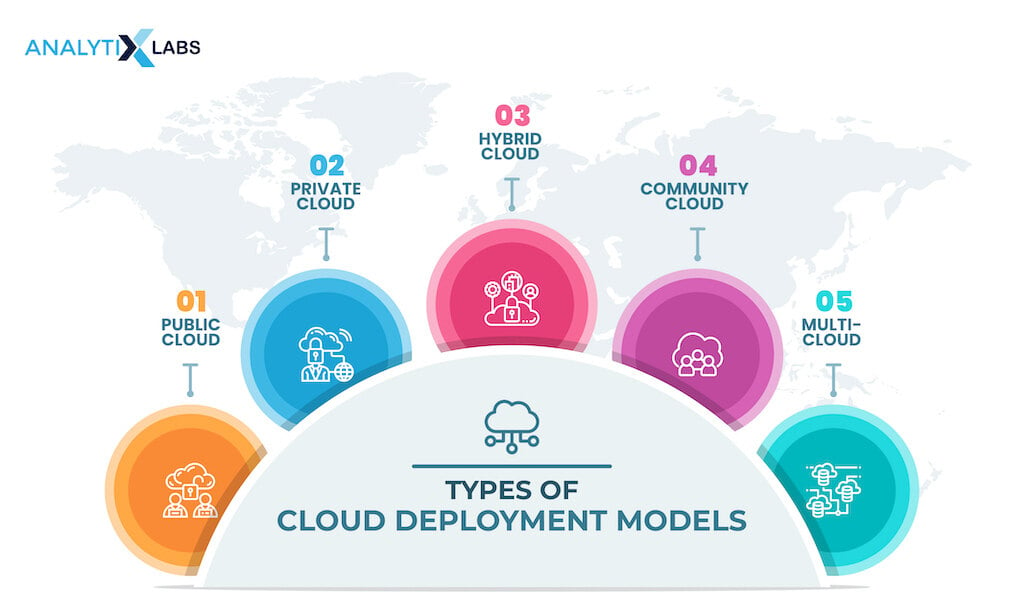
Public Cloud
Public Clouds provide Cloud infrastructure resources to anyone who wants them on a pay-per-use basis. In the public Cloud deployment model, customers use services offered by a third-party provider who manages all aspects of the infrastructure, platforms, and applications over the Internet.
The Cloud provider is liable for maintaining the infrastructure, and customers do not need to pay for costly hardware or maintain complex software programs.
Examples include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.
Advantages
- Low cost – Pay only for the resources you use.
- Scalability – Easily increase or decrease capacity as needed.
- High availability and reliability – Access to global data centers and Cloud infrastructure.
- Security – TProvider is responsible for the security of all data stored in the public Cloud.
Disadvantages
- Security concerns – Data stored on a shared infrastructure is less secure than on a private Cloud.
- Compliance requirements – Public Cloud may not meet the security requirements for all applications.
- Cost concerns – Be aware of costs associated with growth or usage spikes.
Private Cloud
A private Cloud deployment model provides on-premise, enterprise-level computing resources that are dedicated to one customer. It provides complete control to the customer over the infrastructure, applications, and data managed in the private Cloud.
Generally, a private Cloud setup is implemented within an organization’s IT infrastructure. It also requires more upfront costs than a public Cloud. However, customers benefit from customized services tailored specifically to their needs.
Examples are VMware vCloud Suite, Microsoft Azure Stack, OpenStack, and Cloud Foundry.
Advantages
- Personalized and adaptable growth – Customers can customize the setup to adjust the required storage, processing power, and other resources.
- High scalability – Allow customers to add and remove resources as needed.
- Strong security – Encrypted customer data and authorized access only.
- Privacy and reliability – Secure customer data with strict access control.
Disadvantages
- High costs – Upfront investment can be large and, in some cases, prohibitive.
- Maintenance overhead – IT staff must monitor the environment regularly to ensure it runs efficiently.
- Complexity – Managing a Private Cloud requires specific expertise and skills that may not be readily available.
Hybrid Cloud
A hybrid Cloud deployment model combines the advantages of both public and private Clouds, allowing customers to store sensitive data in-house while taking advantage of Cloud scalability when needed.
In addition, hybrid models offer more flexibility than either single platform alone, as they allow organizations to use the right technology for each workload, optimizing their IT infrastructure costs using the necessary and available resources.
Advantages
- Flexibility – Ability to combine public and private Clouds with meeting business needs
- Scalability – Easily increase or decrease capacity as needed.
- Improved performance – A mix of Cloud and on-premises resources enables organizations to use the best technologies for their application needs.
- Cost savings – Ability to leverage both public and private Clouds for cost-savings, depending on usage and workloads.
Disadvantages
- Security – Protecting data across multiple Clouds is difficult.
- Management complexity – Managing different Cloud providers and applications can be complex and challenging.
- Integration issues – Ensuring applications can communicate with each other across multiple platforms can pose a challenge.
Community Cloud
A Community Cloud allows companies to share resources, collaborate on projects, and communicate with each other. It employs many Clouds to fit the demands of a user group, business, or area of expertise.
All participants can access the same data in real time from any device connected to the Cloud platform, ensuring secure and up-to-date information is always accessible. It bridges communication gaps between organizations by enabling seamless collaboration between different departments.
Advantages
- Affordable – The cost of deploying a community Cloud is usually much cheaper than in-house solutions, as the services are shared among multiple organizations.
- Enhanced Security – With data stored in one secure location and managed by the Cloud provider, there is less risk of data breaches that could occur from malicious actors or outdated hardware/software.
- Improved Collaboration – With all members accessing the same information, any changes or updates can be easily made and applied across the board with minimal effort. It becomes easier for teams to work together on projects from different locations.
- Increased Flexibility – Community Clouds allow organizations to quickly deploy applications and services without investing in costly hardware or software infrastructure. This helps businesses remain competitive in a changing market where innovation is key.
Disadvantages
- Security and Privacy – As community Clouds involve multiple organizations, it is more difficult to ensure data security. It could lead to potential privacy issues if the data is shared with third parties or other members of the community Cloud.
- Costs – The costs associated with maintaining a community Cloud can be high, as each organization needs to pay for its portion of the overall infrastructure. Additional fees may also be associated with services such as storage or bandwidth usage.
- Reliability and Availability – Community Clouds involve many different organizations, and they are often subject to outages that can harm operations. Furthermore, some organizations may not have access to reliable internet connections, which can further hamper performance.
Multi-Cloud
A Multi-Cloud deployment model refers to the simultaneous usage of several public Cloud services from several suppliers within a single architecture. One such scenario is for a company to use Amazon for data storage, Google Cloud Platform for development and testing, and Microsoft Azure for disaster recovery.
The single vendor’s inability to properly address an enterprise’s needs is typically the driving force for the multi-cloud concept. A business that uses many Cloud providers can also prevent data loss or downtime brought on by a single vendor’s failure.
Advantages
- Resilience – By using multiple Cloud service providers, organizations can ensure that the availability of their applications and services remains constant, even if one of the Clouds fails.
- Cost Savings – A multi-cloud strategy enables organizations to save money by using different pricing plans from multiple vendors. It helps reduce costs without compromising on quality.
- Scalability – With a multi-cloud strategy, businesses can easily scale up and down to meet their customers’ demands.
- Security – With more than one provider involved, there is less chance for malicious activity to affect all of the data. In addition, each vendor provides its own security measures and protocols, making it difficult for attackers to access sensitive information.
Disadvantages
- Increased complexity – It involves the complexity of managing multiple vendors, security and compliance risks associated with using different Cloud providers, and the cost of subscribing to various services.
- Higher demands for skill – Working with multiple Cloud providers requires personnel with expertise in each system.
- Lack of Interoperability – Each Cloud platform is created differently, meaning moving applications from one provider to another may be difficult.
- Higher Costs – Purchasing services from multiple vendors and managing them effectively can be expensive.
Approach to Cloud Deployment
Effective Cloud deployment depends upon the organization’s requirements. The approach to Cloud deployment should include identifying the need for a Cloud system, assessing the available options, and choosing the best one. It must also consider an organization’s current infrastructure, budget, and other constraints that can affect a successful deployment.
The commonly used Cloud deployment models are:
SaaS – Software as a Service
Software as a service is a software licensing and distribution paradigm where your entire application stack is supplied as a Cloud service. The software program and its supporting infrastructure are centrally hosted on a vendor’s Cloud service and receive complete maintenance and updates from them.
It eliminates the need for complex network setup and hardware purchases. With SaaS, users can access their applications on any device with an internet connection without worrying about setting up or maintaining anything on their own servers.
Additionally, businesses can avoid costly IT infrastructure investments required for traditional software deployment models as the vendor oversees application support and maintenance.
SaaS Cloud deployment does not require vendor-required downloads or installations on your end. Among other current computer infrastructures, popular examples of SaaS include Google Workspace, Microsoft 365 Slack, InfinCE, and ReachOut Suite.
PaaS – Platform as a Service
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a Cloud service category that provides users access to a scalable and flexible Cloud platform for building, deploying, and managing apps. PaaS solutions provide the underlying infrastructure for creating and managing applications, including hardware and software. They are designed to make it easier for developers to create and deploy apps without worrying about scalability or infrastructure issues.
PaaS solutions offer a range of advantages for businesses, such as enabling faster development time by providing pre-built modules that can be reused in multiple applications. As a result, companies can leverage cost savings from shared resources and economies of scale.
It offers scalability so companies can quickly add features or services when needed. Advanced security measures make them better than traditional web hosting providers. PaaS solutions often have built-in analytics tools that help users better understand app usage and performance.
IaaS – Infrastructure as a Service
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a Cloud service model that provides access to virtualized computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking. It allows businesses to use Cloud-based services without investing in physical infrastructure.
IaaS solutions are ideal for organizations that need flexible, scalable solutions but do not have the capital or technical expertise required to build their own data centers or manage their own IT infrastructure. With Infrastructure as a Service, customers pay only for what they use and benefit from the economies of scale associated with Cloud computing.
IaaS enables customers to spin up virtual machines (VMs) in minutes and customize them with the operating systems and applications needed for their specific use case.
Furthermore, many IaaS providers offer advanced features such as auto-scaling and application performance monitoring that further accelerate deployment times and optimize resource utilization.
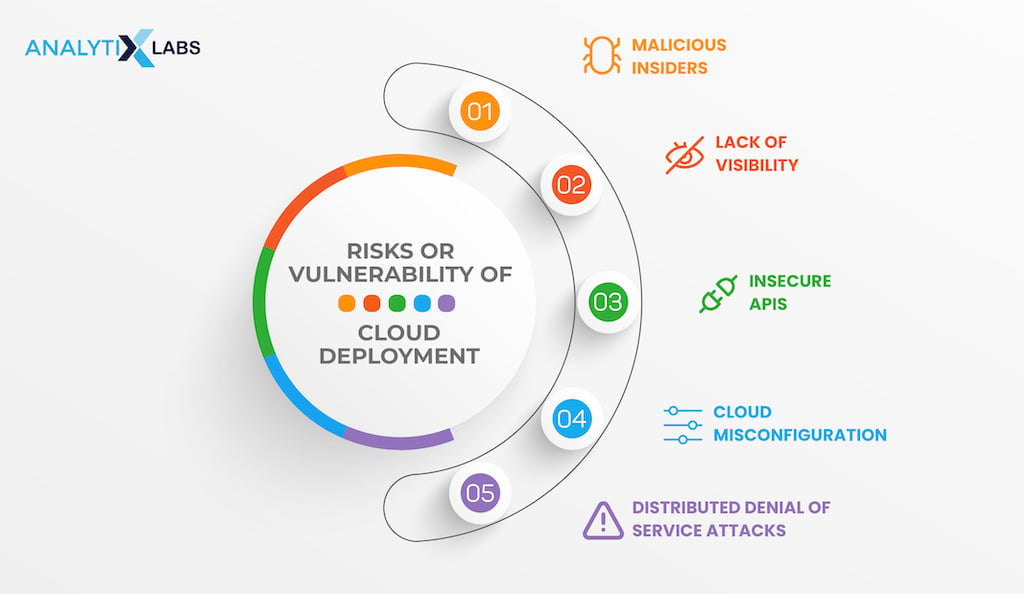
Risks or Vulnerability of Cloud Deployment
-
Malicious Insiders
Cloud providers may not have adequate security controls to detect malicious insiders who can easily access and modify data. Finding a malevolent insider on the Cloud is challenging because there is no control over the underlying infrastructure. Many standard security solutions are also ineffective.
-
Lack of Visibility
The infrastructure used by a company’s Cloud-based resources is not part of the corporate network or owned by the company. As a result, organizations may not have full visibility into the environment.
This can make it tough to detect security threats and track changes in data over time. A significant problem is it might delay responding to threats and can lead to a data breach. It is essential to follow a proactive security strategy.
-
Insecure APIs
APIs, or application user interfaces, are a well-liked technique for streamlining Cloud computing. These APIs can be vulnerable if the proper security measures are not in place, leading to potential breaches of confidential customer data or other sensitive business information.
-
Cloud Misconfiguration
One of the main reasons for Cloud data breaches is incorrectly configured Cloud security settings. If the Cloud infrastructure is not configured correctly, access control policies might fail to be enforced, and data can be stored in unsecured areas.
It is simple for a misconfiguration or security oversight to occur and leave an organization’s Cloud-based resources exposed to attackers. Many organizations lack experience protecting Cloud infrastructure and frequently have multi-cloud deployments, each with a different set of vendor-provided security controls.
-
Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacks
Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks are illegal attempts to bring down a website or other web service. These attacks are designed to disrupt the availability of a service or website by overloading it with traffic from multiple sources. Cloud infrastructure is particularly vulnerable to DDoS attacks because its scalability allows attackers to flood networks with more requests than before.
Many Cloud providers have built-in defenses for DDoS attacks. However, organizations should still employ additional security measures, such as DDoS protection services and monitoring their network traffic for suspicious activity.
Choosing the Right Cloud Deployment Model
Choosing the right Cloud deployment model can be tricky. Here are some steps you can take to make sure you choose the best Cloud deployment model for your business:
- Assess Your Requirements: Take time to analyze your organization’s needs and requirements when selecting a Cloud deployment model. Consider factors like budget, performance goals, security requirements, and scalability needs to ensure you pick the most suitable solution for your business.
- Research Options: Once you have determined what type of Cloud deployment model is necessary for your organization, research each option thoroughly. Understand how each one works and what features and benefits each one offers.
- Evaluate Resources: Consider the resources available when selecting a Cloud deployment model. Ensure you understand the hardware, software, and personnel required to implement the chosen option.
- Compare Costs: Compare the costs associated with each Cloud deployment model before deciding to ensure you get the best value for your money.
- Monitor Performance: Once you have implemented a Cloud deployment model, monitor its performance closely over time to ensure that it continues to meet all of your requirements and needs as changes occur within your organization or in the technology industry.
- Make Adjustments: Make any necessary adjustments to your chosen Cloud deployment model over time based on changes in requirements or preferences or as new products and services become available that better fit your needs.
- Have a Backup Plan: Finally, be sure to have a backup or recovery plan in place if something goes wrong with your Cloud deployment model.
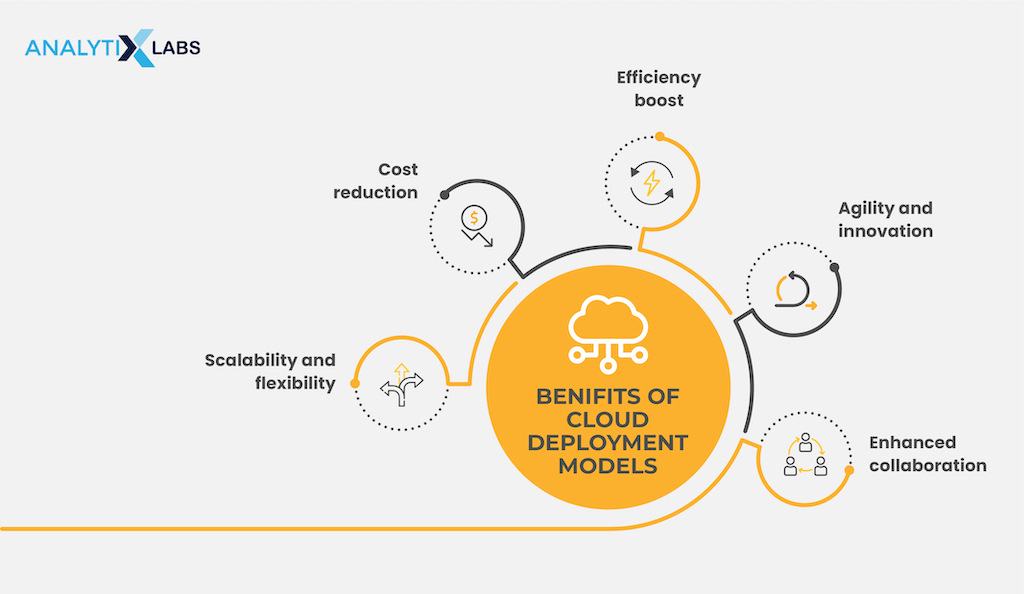
Benefits of a Cloud Deployment Model
Cloud computing offers several benefits over the conventional method, including:
- Scalability and flexibility- Businesses may readily access and process data without needing extra cash, thanks to the connectivity to various servers made possible by Cloud-based infrastructure. With the scale computing ability to meet client needs, businesses can remain relevant in a competitive climate.
- Cost reduction- By using Cloud models, businesses can spend less on infrastructure and equipment.
- Efficiency boost- By allowing businesses to reduce on-site equipment and personnel, Cloud computing can help enhance the efficiency of everyday operations.
- Agility and innovation- The agility of Cloud computing makes it easier for businesses to innovate and launch new services quickly and helps them stay ahead in the ever-changing market.
- Enhanced collaboration- By leveraging Cloud technology, teams can share documents in real-time, enabling them to work together more effectively across various platforms. Additionally, remote workers can access files from anywhere with an internet connection. It boosts productivity and allows for better visibility into project progress.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the three types of Cloud deployment models?
Three subcategories of Cloud services are
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
SaaS is an application that customers can access over the Internet. It requires minimal setup on the customer’s part and is typically provided for free or a fixed fee.
PaaS provides more features than SaaS but still requires minimal setup from customers. It offers software development tools such as databases, web servers, and operating systems that are helpful for building applications on top of it.
Third-party providers fully manage IaaS and provide customers with virtualized computing resources like storage, servers, and networking services. IaaS is the most flexible and expensive option, requiring customers to configure and manage their own infrastructure.
- What is a Cloud deployment model example?
A common example of a Cloud deployment model is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). It is a Cloud deployment model that allows customers to rent or purchase hardware and software infrastructure such as servers, storage, networks, and more on a pay-as-you-go basis.
With IaaS, the Cloud provider manages the underlying hardware resources while allowing customers to maintain control over their applications and data.
Other examples of Cloud deployment models include Platform as a Service, Software as a Service (SaaS), and Function as a Service (FaaS). Each model offers different levels of control for users based on their needs.
- Why use Cloud deployment?
Cloud deployment is a great way to quickly and easily deploy applications. Organizations can scale their environments as needed and reduce their reliance on hardware. They can save money on resources such as server maintenance and upgrades. While also taking advantage of the cost-effectiveness of the Cloud.
Additionally, Cloud deployment allows users to access resources anywhere at any time with minimal disruption.








