With data being a vital asset for any business ranging from finance, healthcare, social media, energy, retail, real estate, manufacturing, it is highly important to know how to analyze it. However, the data itself is raw, unstructured without any meaning. To get meaningful insights into this data, we need to know the ways and types of business analytics, which allows us to understand what the data reflects and how it can be used. In this article, we will explore the types of data analytics.
There are broadly five types of business analytics. The types are implemented in stages and are interrelated. Each of these types is an essential building block for a business to know and offers a different insight. This helps us to know what is currently happening in the company to what might happen, and what solutions and steps could be adopted to optimize functions. Equipped with the right choice of analytical tools and techniques, one can gain deeper insights into the data, informed recommendations, and make better decisions.
Related: What is Business Analytics? Different components, tools, skills and career.
AnalytixLabs is India’s top-ranked AI & Data Science Institute and is in its tenth year. Led by a team of IIM, IIT, ISB, and McKinsey alumni, the institute offers a range of data analytics courses with detailed project work that helps an individual fit for the professional roles in AI, Data Science, and Data Engineering. With its decade of experience in providing meticulous, practical, and tailored learning. AnalytixLabs has proficiency in making aspirants “industry-ready” professionals.
What Are the Types of Analytics?
The different types of analytics are as follows:
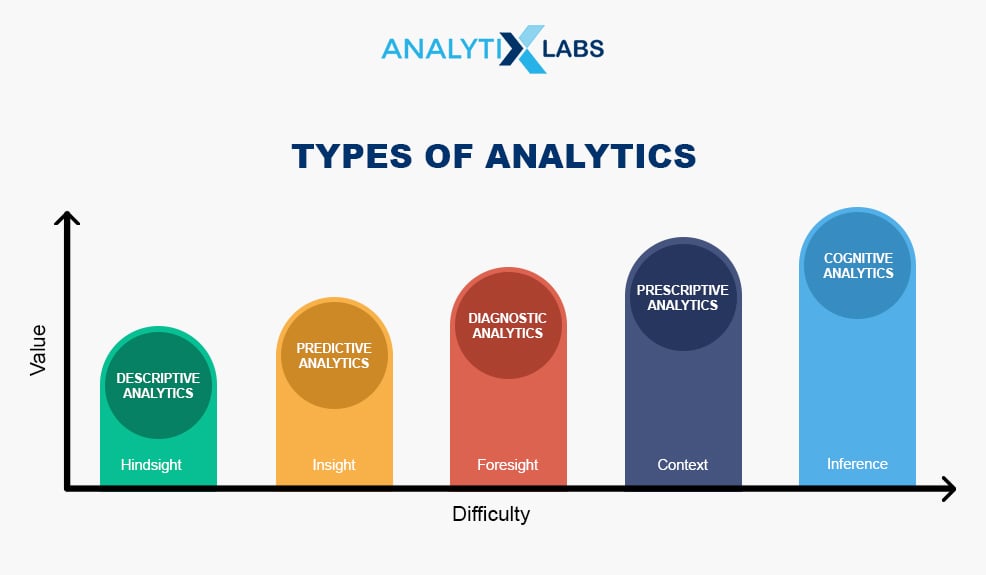
- Descriptive Analytics: It helps in describing or summarizing what has happened in the past.
2. Diagnostic Analytics: This focuses on the past performance to ascertain why something has happened.
3. Predictive Analytics: Using all the past gathered data tells what is likely to happen on a granular level. The prediction of the possible outcome is made using statistical models and machine learning techniques.
4. Prescriptive Analytics: It is a type of predictive analytics used to recommend one or more courses of action on analyzing the data.
5. Cognitive Analytics: It brings together several intelligent technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning algorithms, deep learning models to mimic the human brain to derive results from matching human thinking.
Types of Business and Data Analytics
Descriptive Analytics

This first type of analytics provides the facts stating what has happened. It is the simplest type that “allows you to condense big data into smaller, more useful nuggets of information.” It is the most basic form of analytics performed by more than 90% of businesses. This is the starting point of any analytics and alone comprises 80% of the business analytics. The objective is to summarize the results and to understand what is going on.
Descriptive analytics helps a business learn from its past behavior and how it will impact the future. It provides information that helps to understand the performance of the business on an overall aggregate level. It is also an important step in explaining the current raw data to the various stakeholders.
This is more like a management information system (MIS), where an MIS gathers data from multiple online systems, analyzes the information, and reports data to aid in management decision-making. The key techniques used are data aggregation and data mining to summarize the past data of understanding the data’s underlying behavior and not for any predictions.
These are the start of the data analytics value chain and are the most valuable to uncover any patterns. A simple example of descriptive analytics is to assess credit risk: we can predict a consumer’s likely financial riskiness by seeing their balance amount against the credit limit. It is also used to analyze the sales cycle of a store. Also, it can be used to categorize the customers based on their product preferences, purchase transactions, how often they purchase. In the context of social media, descriptive analytics offers an overview of the performance metrics: the total of posts, mentions, followers, comments, page views, reviews, the average time is taken to respond, and so on.
Diagnostic Analytics

Diagnostic Analytics is the second type of data analytics. Like descriptive analytics, this also focuses on the past and ascertains why something has happened. It is also known as root cause analysis because it looks deeper to understand the events’ root cause. It allows us to isolate the patterns to identify these patterns’ source and the factors that affect the business. The diagnostic analytics helps to understand, for instance, why there has been a sudden surge or decrease in sales.
This type also helps detect the anomalies and determine the causal relationship for the cause and effect present in the data. It is characterized by discovering data, data mining, and correlations. Some of the techniques employed at this stage are feature importance, principal component analysis, sensitivity analysis, conjoint analysis. To analysis, it mostly uses probabilities, likelihoods, and the distribution of outcomes.
Diagnostic analytics for social media campaigns can refine the descriptive analytics stage data into one view to see what did or did not work in the past campaigns. Retailers can break down the sales and gross profit to various products and subcategories to understand where and why they missed the overall profit margins. Another use case of diagnostic analytics is in healthcare. One can identify the impact of medicines on the patients and can be used to study the effects of before and after treatment.
This type only uncovers and provides the casual relationship, and it can not provide any actionable insights, hence has limitations. That’s why the next two types of analytics are important.
Predictive Analysis

Predictive analytics uses the gathered data and descriptive and diagnostic analytics results to tell what is likely to happen in the future on a granular level. This is where the earlier steps’ insights can be used into actionable insights for decision-making. Its use involves forecasting the future, predicting the market trends, changing customer behaviors, and analyzing competitors to optimize and build strategies to maximize the business results.
The predictions are made by analyzing the past data, detecting patterns, casual relationships in the data, and then extrapolating them in the future. For instance, a bank to predict which customer is likely to default will need all the past data about which customers have defaulted to predict. The inferential statistics, training algorithms for regression, classification, and segmentation come under this type of business analytics. It uses the techniques to segment the data into groups, apply clustering methods, heuristic rules, decision trees to project future outcomes.
The predictive analysis can also be used to generate, test, and evaluate hypotheses. It is useful to understand whether a set of features are explaining or predicting other features. For example, it can validate a person’s hypothesis inhibiting from a certain region, age group, gender defaults in its credit card payments. This is especially useful when some of the features are actions determined by the business decision-makers. One of the applications of prescriptive analysis is sentiment analysis.
Predictive analytics is extensively used in every industry: finance, healthcare, social media, sports, energy, manufacturing. One of the most frequent applications is in retail, where the retailers are always using predictive analytics to predict and improve their sales positions. Amazon’s recommendation engines are a classic example where on making one purchase, the engine shows the list of other similar items that the buyers have purchased.
Prescriptive Analytics

Building on predictive analytics, prescriptive analysis is the next step that helps in exploiting the future. It essentially tells the business what should be done. Using simulation and optimization, it advises on the possible outcomes and suggests actions that can maximize the key business metrics. The focus here is on how to make it happen.
It can be defined as a business optimization data analytics that provides insights on “what should a business do” to solve a problem. It explores several possible outcomes and suggests actions depending on the results of descriptive, diagnostic, and predictive analytics of the data. The prescriptive analysis uses a feedback system that constantly learns, updates the relationship between the action and the results.
It does not predict one possible future but rather multiple future outcomes. It is an advanced analytics concept based on optimization and simulation. Optimization helps understand how to achieve the best outcome and identify the data uncertainties to make better decisions. The other approach of prescriptive analytics is a simulation in which all the key performance areas are combined to design the correct metric goals. This ensures whether the key performance metrics are included in the solution.
The prescriptive analysis is performed when scenario analysis simulates the future under various sets of assumptions and combines it with different optimization techniques. It uses statistical models and machine learning algorithms to estimate the probabilities, optimizing and recommending actions. A prescriptive model can recommend the best course of action for any pre-specified outcome as it can predict the possible results based on a different choice of action. Waymo, Google’s self-driving car, is an example of prescriptive analytics. Recommendation engines are a use case of prescriptive analysis.
Prescriptive analytics can be applied to almost any industry where the population is to be targeted or grouped. It also has its applications in marketing, financial markets, and the transportation industry. In social media, grouping the customers under one bucket based on their characteristics can use prescriptive analytics to optimize the offering to each group. Similarly, it can be applied in the transportation sector to save time and resources by optimizing the best routes. In the financial markets, the researchers heavily rely on statistical modeling to maximize the returns and manage risk and profitability.
Cognitive Analytics

This is the most advanced type of business analytics that applies human intelligence to certain tasks by combining many technologies such as artificial intelligence, semantics, machine, and deep learning algorithms. The goal is to understand and mimic how a human brain makes a decision and comes with a system or computer that does the same. Some of the tasks that can be performed using cognitive analytics are chatbots, virtual assistants, recognizing objects in an image, and segmentation of those images.
Cognitive Analytics works by searching the entire available “knowledge base” to locate real-time data. It is highly dependent upon and often combines artificial intelligence techniques, machine learning, deep learning, neural networks, and semantics. It mimics the human brain to study and learn from the available data to extract actionable insights hidden behind data patterns. It collects and makes real-time data sources such as text, images, audio, and video available to these analytics tools for decision-making.
You can get our premium business analytics learning materials and learn all the fundamentals and advanced aspects at your convenience, or you can book a demo with us.
Conclusion
The analytics spectrum comprises these different types of business analytics that allow a business to understand and learning from past patterns. These data analytics types are the catalysts that help improve predictions and take recommended actions for the future. These may seem to appear to be applied sequentially, but these can be implemented congruently. Knowing when to employ the relevant form of analytics helps develop the right business solutions and gives a competitive advantage.
FAQs – Frequently Asked Questions
Ques. What are the 3 types of business analytics?
The three primary types of business analytics are:
- Descriptive Analytics: that tells what has happened in a business
- Predictive Analytics: what could happen in a business, and
- Prescriptive Analytics: what should happen in a business
Ques. Which type of analytics is the most important for businesses in general?
Prescriptive analytics is the most important type of business analytics. It tells what will happen in a business and how it could happen if taken certain steps. It results in rules and recommends the action steps to be taken. Given its power to suggest appropriate actions, prescriptive analytics is preferred, and also cognitive analytics has disrupted the industry, and both are the front-runners in this spectrum.
Ques. How many types of data analytics are there?
There are four types of data analytics:
- Descriptive Analytics: what has happened?
- Diagnostic Analytics: why it happened?
- Predictive Analytics: what is likely to happen in the future?
- Prescriptive Analytics: what is the best course of action?
- Cognitive Analytics: applies human-like intelligence to drive results.
Ques. What is the difference between cognitive analytics, predictive and prescriptive analytics?
Cognitive Analytics applies human-like intelligence to certain tasks. It combines technologies, such as semantics, artificial intelligence algorithms, deep learning, and machine learning, to learn from the interactions with data and humans. On the other hand, predictive analytics tells what is likely to happen in the future, and prescriptive analysis tells what action could be taken.
If you have any questions or want to share your feedback then do reach out to us in the comments section below.
You also like to read:
1. Top 25 Puzzles for Business Analyst Interview2. Evolution of Business Analytics | Business Analytics Future
3. Difference Between Data Analysis and Interpretation – An Overview









1 Comment
A great website with interesting and unique material what else would you need.