- Multi-platform
- Open-source
- Lightweight
History of R programming language
R is a low-level language created to implement the S language easily. This language was created by Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman in 1995 (and released in 1997) as a part of the GNU project. This project used the GNU operating system and its packages to create free software and has since been maintained by the R foundation – a non-profit organization. As a result, it is free and functions under the GNU General Public License in source code form provided by the Free Software Foundation.
In order to perform computationally heavy operations, low-level languages such as C and C++ can be linked with R. Users can even write code in C to manipulate the R’s objects. R has a very strong concept of the environment within which a number of functions lie that are accessible through libraries/modules.
These libraries can be extended by the users by creating their own functions to perform operations in R and making them publicly available through CRAN (Comprehensive R Archive Network) which is a family of connected servers that provide R with unprecedented functionalities. A number of times these libraries are written in a language like C while the user writes the code in R, making R more efficient and faster than several other languages.
What is R Programming Language?
To understand what is R programming language, it is essential you know the history of this language and its place in the data science world. R is mostly used to perform statistical computing i.e. performing statistical tests on data to develop statistical models. R is an object-oriented language, which means every operation in R is performed around objects. These objects can be anything that can be stored in a variable, like one-dimensional data structures, two-dimensional data structures, user-defined functions, etc.
R is relatively easy to learn considering it is a low-level language. This is another reason why it requires longer codes. However, when pitted against other low-level languages like C, R is relatively one step higher. Add to this, R is a dynamically typed language which means the user doesn’t have to declare the variables. R automatically detects the class, which makes coding in R quick.
Read: Why R is a preferred language over SAS?

The biggest reason why R is so popular is that R is a modular open-source language. This makes R an ever-expanding language, Users can create their own modules/libraries and share them in the community. Consequently, R has a vast community that provides support, troubleshooting, and expansion of R’s functionalities.
As of 2021, there were more than 15 thousand libraries in the CRAN repository. The libraries and vast community have enabled R to become a tool that not only performs statistical computing but can also perform Data Mining, Visualization, Machine Learning, and even Deep Learning. In addition to this, R can run on a wide range of UNIX-based platforms including popular ones such as Windows and macOS.
Basics of R Programming Language
R is a vast programming language and there are a number of aspects that one needs to pay attention to in order to properly understand this language. A number of basic concepts of R language include-
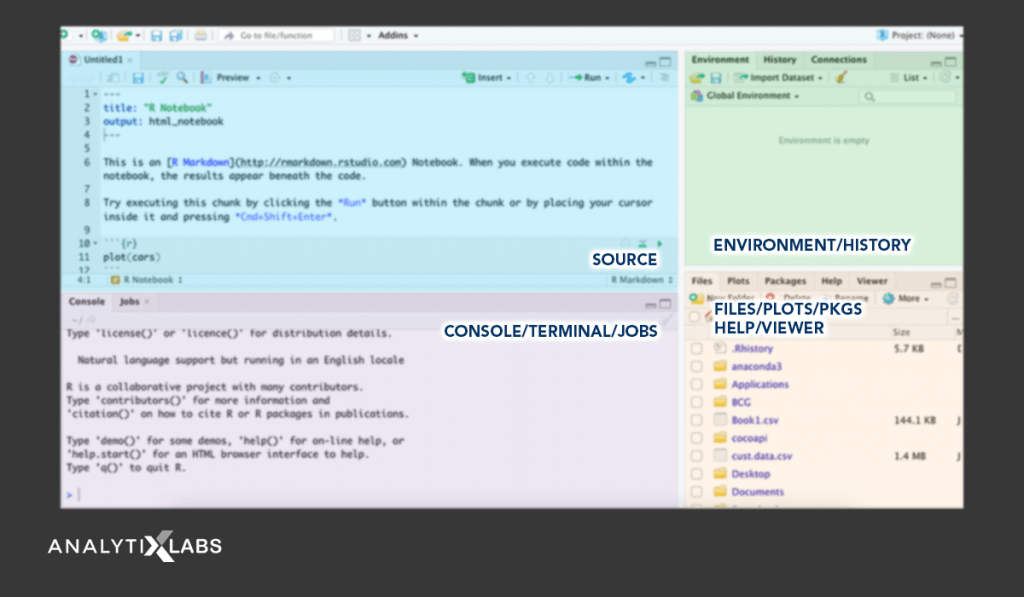
(1) Objects and Environment
Being an object-based language, in R anything that can be saved in a variable is known as an object. In turn, all the operations in R are performed on or around these objects. The class of the object determines the associated functions that can be used to manipulate these objects. The data type or the data structure of the object determines the class of the object.
All these objects are shown in the Environment window. This makes managing objects extremely easy as the user can see the objects that are currently occupying the space in RAM. The user can export, and import objects using a .RData file and can even delete objects that are unnecessary to make the coding process more efficient. Common functions include:
| Function | Formula |
| Finding all the names of objects in the environment | >> ls() |
| Saving all the objects that are there in the environment | >> save.image(“MyBackup.RData”) |
| Saving one object from the environment | >> save(Cities, file=”cityobj.RData”) |
| Removing an object | >> rm(Cities) |
| Removing all the object from the environment | >> rm(list=ls()) |
| Loading a RData file | >> load(“MyBackup.RData”) |
(2) Console
It is considered the brain of the R programming language and the IDE used for running R- R Studio. In the console, you can write the code, execute it and simultaneously see the output. Any code written in the console, however, cannot be saved in the form of a script. Also, codes that have been already executed in the console cannot be edited. Interestingly, any code that is written in the code window is executed in the console only. Follow the below video by James Cook to get a grasp on the whole concept of the console in R programming language.
(3) Script
Codes written in the code window can be saved as a .R file. This file is commonly known as an R script. These scripts are helpful in sharing and re-using the codes.
(4) Operators
These are symbols that allow us to perform certain operations. For example, the Task performed using the function sum() can also be performed using its operator, like this:
sum(10,20) can also be performed using the + operator -> 10+20
In R there are a number of operators such as:
| Type | Operators | ||||||||||
| Assignment Operators |
= -> <- |
||||||||||
| Arithmetic Operators |
/ (division) * (multiplication) + (addition) – (substraction) %% (modulus) Remainder %/% (Integer Division) Quotient ^ (Power) |
||||||||||
| Relational Operators |
> (Greater than) < (Less than)
<= (Greater than equal to)
>= (Less than equal to)
== (Equal to Equal to) |
||||||||||
| Logical Operators |
& (AND) | (OR)
(7) Data Structures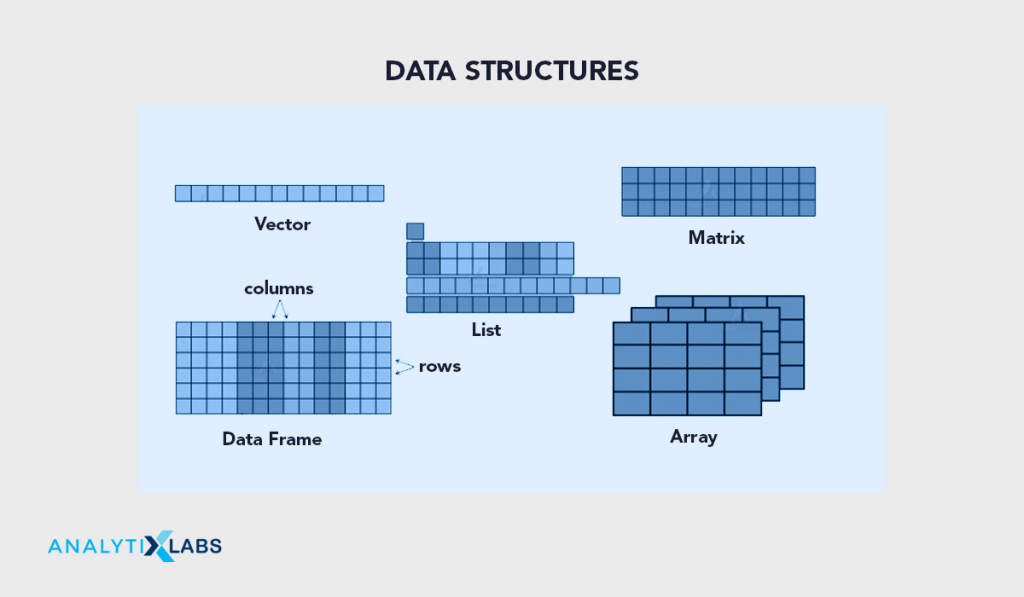 Data Structure is the mechanism for saving multiple elements in an object in an efficient manner. They can be differentiated on the basis of their homogeneity and dimensions. In R the most common data structures are-
(8) Help 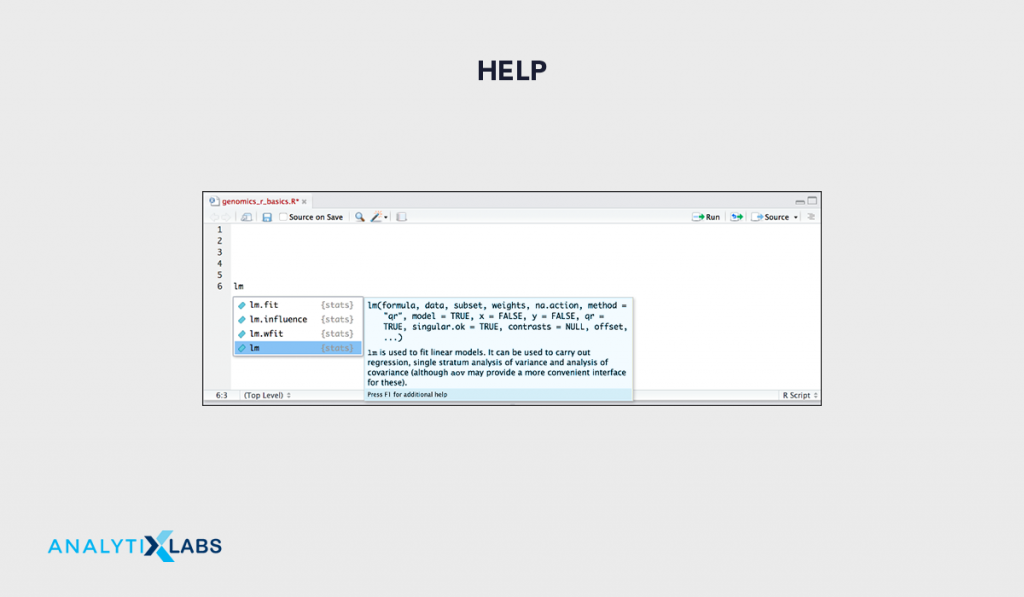 Help is a highly powerful aspect of R where for each function, detailed documentation is provided that the user can use, explore and implement to learn about new functions. One can also press on tab while writing a function to gain some understanding regarding the use of it. Common methods include >> ?functionname >> help(functionname) (9) Packages/LibrariesAs mentioned earlier, R is a modular language, it’s the packages that play an important role in expanding the capabilities of R. In R the packages can be divided into two parts – system and user where system packages are those that are provided by the R by default whereas user libraries are the third party libraries that the user downloads from CRAN Common functions include-
(10) ShortcutsOne can find all the shortcuts available in R and R studio by using the shortcut – Alt + Shift + K Common shortcuts include-
Why Learn R Programming Language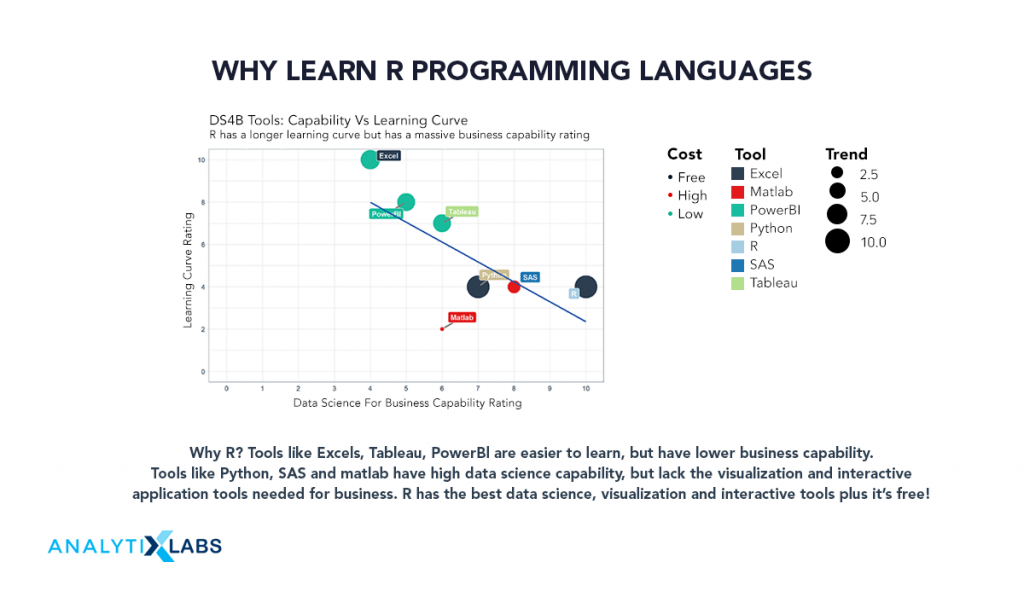 There are several reasons to learn r programming language with the common one being the first one- (1) Comprehensive Data Science ToolR is a comprehensive tool as it can take care of all the major aspects of the data science domain these include-
(2) Ease of LearningR is easy to learn and this is something highly helpful for those who are from a non-computer background. As it is created by statisticians who were not technically computer programmers, the learning curve of R is relatively less steep as compared to other generic computer languages. (3) Large CommunityOne of the biggest advantages of R is its CRAN-driven user community that keeps on upgrading R and keeping it up to date. This makes learning R programming fruitful as with the ever-changing environment where often language becomes obsolete, R has managed to stay relevant all these years. (4) Business FriendlyR with its IDE R Studio provides servers and other services that make it a secure and reliable platform perfect for businesses. This is the reason that R even with being an open-source non-commercial suite, is accepted by a number of companies throughout the world. (5) CompatibilityR can very well integrate with other platforms and frameworks. This includes the ease with which R can be run on Operating systems like macOS, Windows, Linux, etc, and can import data from multiple sources such as MS Excel, MySQL, Oracle, etc. (6) Big DataWith the recent advancement in Big Data Analytics, a tool that has stood out to do this job has been R. It now has the required capabilities to connect to other Big Data-based technologies reviewing its importance in the dynamic world of Data Science. Read: What does R training do to your data science skills Python v/s R
The biggest competitor of R is Python. While they are similar as both of them are modular, dynamically typed, open-source languages with huge communities and are used in solving data science-based problems, there are significant differences also. While R is a language that was made for statistical computing, Python was created as a general-purpose language and it is because of libraries such as NumPy, pandas, and sci-kit learn that data science is possible in python. If compared, R is a more non-standardized language which sometimes causes it to be slower than python. Python has more number IDEs whereas for R the only common IDE is R Studio. While integration is good in R, Python’s integration is even better which often makes it a tool for performing end-to-end projects. In the real world, the share of R is relatively less than python, however, in the field of academia startups, and research, R sometimes outshines python. For a more detailed comparison, read our blog on Python vs. R vs. SAS How To Learn R Programming Language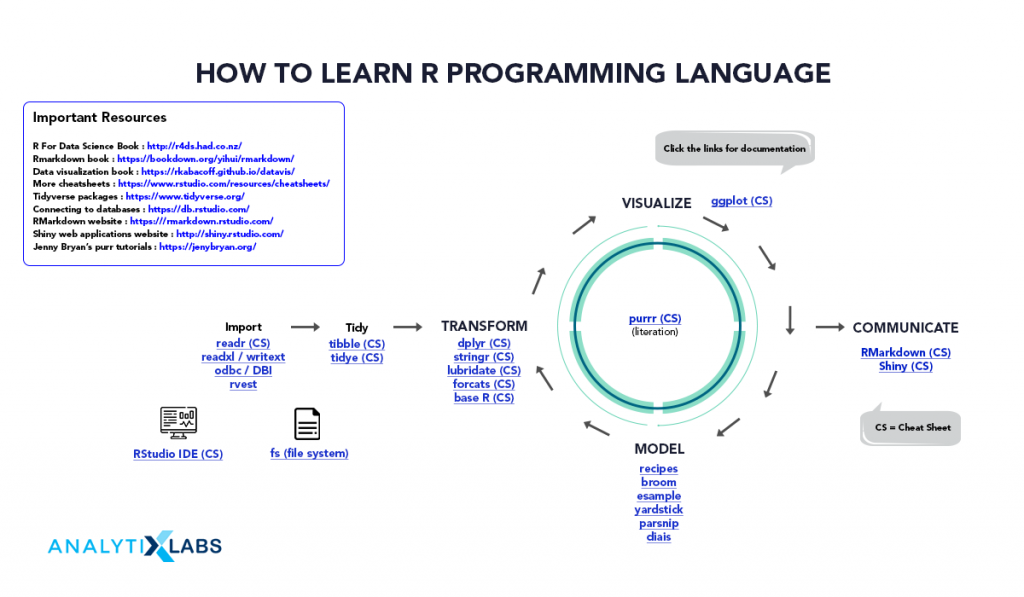
In order to learn R programming language, you can use multiple platforms. This includes academic courses on R common during bachelor’s or masters in economics, statistics, data science, and sometimes computer sciences. You can also learn R from online courses run by Data Science Institutions such as AnalytixLabs, Jigsaw, etc. Another great way to learn R is from books and blogs on R. However, the important thing is to concentrate on aspects of R that can help the user to learn R quickly and efficiently. Read: Learning tip 101: Learn R Programming Language to stay relevant These important aspects are as follows- 1. Understanding R Fundamentals In order to learn about R, one must start with the fundamentals mentioned above. No matter how advanced you get into R, the fundamentals will support you throughout. Therefore, having a good knowledge of data types, structures, loops, classes, functions etc is important. 2. Exploring Important Packages There are more than 15,000 packages in R, thus it becomes important to know which libraries to explore first to reach a decent lever in R as not all libraries are of equal importance. Some of the Common Packages / Libraries include
3. Implementing Documentation One must learn how to read the help section of a function, explore the sample examples, understand the use of various arguments and implement them. This is the best way to expand on the knowledge of the functions. 4. Learning Statistics, Algorithms, and Business No data science project works in a void. The knowledge of R needs to be complemented with knowledge of statistics (descriptive statistics, hypothesis testing, regression, etc), understanding of the various machine and deep learning algorithms and a good knowledge of how various business domains function and the issues they face. This helps in converting the programming prowess into providing a viable business solution. 5. Create Projects Lastly, one must create projects. If datasets are not provided to you by your company or client then you must take publicly available datasets pertaining to different domains and apply all the knowledge of Data Science – Data importing, manipulation, mining, visualization, modeling, etc in R. This is the best way to gain confidence regarding the tool you are using. Thus, the question of how to learn R programming language is a complex one as one needs to take care of multiple aspects of this language. Frequently Asked QuestionsQ1. What is an R Programming Language used for? R programming language is used for data mining, visualization, statistical modeling, and creating predictive models using Machine Learning and Deep Learning algorithms. Q2. Is it hard to learn R? The R programming language does have a steep learning curve, however, if one pays attention to its fundamentals and learns how to go through the function’s documentation, it can be easy to learn. Also, if compared to other traditional languages such as C, C++, Java etc, it is extremely easy.  Q3. Is R Language in Demand? As of 2022, most of the fortune 500 companies use R for solving their data analytics-based problems. Also, among the most popular data science languages, it is considered among the top 3. Also, especially in start-ups and research, knowledge of R is in demand. Here’s a quick overview of how your career will shape after you complete an R training program. ConclusionThere are a number of tools that can help data science aspirants in implementing their knowledge, however, R stands out. It is because it is a unique language in the sense that it’s not a conventional programming language and is custom made for solving statistical and by extension data science-based problems. With the rapid adoption of data science across the globe, the demand for R is at an all-time high. Thus, along with other tools, one must have a decent knowledge of R even if it’s not their primary tool. Going forward, the reader must start with reading and doing some research on the basics of R mentioned before and expand on the knowledge of R gained from this article. ! (NOT) |
(5) Syntax Rules
The syntax of the R programming language is something that can be understood as we explore various functions in R, however, there are a number of basic syntax rules that one must know such as-
- Case Sensitivity
- Any object name (including any name of the library, function, etc) should be written in the exact same case as required.
- For example,
- print()This function name is in the lower case and it should be executed as such and a command such as Print() will give an error of function not found.
- View() function requires the first letter to be in the upper case
- If we create objects with the same name but in different cases then those objects are considered separate i.e. city and City will be considered as two different objects.
- The use of comments
- We use the # symbol to create a comment
- All the comments in R are to be preceded by the # symbol
- Naming Rules
- When creating objects in R, one must make sure that the name of the object doesn’t start from a number, doesn’t have any symbol (. and _ are acceptable symbols generally used in the object name to denote space) and doesn’t coincide with another pre-existing function or object.
(6) Data Types and Type Casting
There are various types of data types in different languages which help in performing functions on the objects. In R, we have multiple kinds of data types but the major ones are as follows:
Data type related to Numbers
- numeric
- The most commonly used and found data type in R
- It includes-
- short numbers with decimal
- long numbers with decimals
- short numbers without decimal
- long numbers without decimals
- integer
- It is found in special cases during the importing of certain files or when a certain package’s function output is pre-coded to have this as the output’s data type
- It has no major advantage over the other type i.e. numeric especially if the user has a decent memory
- Only small numbers without decimal can have an integer as the data type
- Definition of a small number is a value between -21474763648 to 21474763647
- complex
- These are the real + imaginary numbers
- for example = 5+6i
- They are very rarely used in day to day operations
Data type related to characters (text)
- character
- It is used to store any alphabets or alphanumeric or symbol
- factor
- This data type is unique to R. Here the values can look like a character to the user, however, internally the values are stored in the form of levels which are represented in the form of numbers.
Data related to Boolean
- logical
- This is the data type that is used to represent the Boolean i.e. TRUE ad FALSE
- All the relational and logical operators provide us with a Boolean output
Date and Time
- Date and Time generally are not a naturally occurring data types in many languages such as R and Python
- These are derived data types i.e. we have to manually convert the object into this data type.
- Date
- This is the data type for denoting dates in R
- POSIXct (Portable OS Interface Exchange)
- POSIX is the data type in which dates are stored in all the OS
- ct is the conversion of POSIX to R
To find the different data types in R we have a function known as a class()
For changing the data types, a process also known as type casting requires functions such as as.character(), as.factor(), as.numeric() etc. However, before changing the data types one must be aware of the hierarchy of typecasting where the highest data type is character and lowest is logical and a higher data type cannot be converted to a lower data type apart from a few specific exceptions.
(7) Data Structures

Data Structure is the mechanism for saving multiple elements in an object in an efficient manner. They can be differentiated on the basis of their homogeneity and dimensions. In R the most common data structures are-
- vector: 1 Dimensional Homogeneous Data Structure
- matrix: 2 Dimensional Homogenous Data Structure
- data.frame/data.table: 2 Dimensional Heterogeneous Data Structure
- list: A mechanism to contain other objects inside of it
(8) Help

Help is a highly powerful aspect of R where for each function, detailed documentation is provided that the user can use, explore and implement to learn about new functions. One can also press on tab while writing a function to gain some understanding regarding the use of it.
Common methods include
>> ?functionname
>> help(functionname)
(9) Packages/Libraries
As mentioned earlier, R is a modular language, it’s the packages that play an important role in expanding the capabilities of R. In R the packages can be divided into two parts – system and user where system packages are those that are provided by the R by default whereas user libraries are the third party libraries that the user downloads from CRAN
Common functions include-
| Functions | |
| To find all the libraries available in the CRAN repository | available.packages() |
| To find all the installed packages | installed.packages() |
| To load a library | install.package(“library name”) |
| To load a library | library(libraryname) |
(10) Shortcuts
One can find all the shortcuts available in R and R studio by using the shortcut – Alt + Shift + K
Common shortcuts include-
- Control +Enter 🡪 Execute the code
- Control + Shift + N 🡪 Creating new R Script
- Control + S 🡪 Saving the R Script
- Control + L 🡪 Clears the console
Why Learn R Programming Language

There are several reasons to learn r programming language with the common one being the first one-
(1) Comprehensive Data Science Tool
R is a comprehensive tool as it can take care of all the major aspects of the data science domain these include-
- R programming
- Creating User-defined functions
- Automating certain tasks through loops etc
- Data Manipulation, Data Mining, and Data Visualization
- Almost all things done in MS Excel and SQL can be done in R
- Can perform all the Statical concepts that other languages such as SAS and SPSS can do
- This includes simple descriptive stats and applied inferential stats
- It can be used to create complex graphs
- Web Application
- R Shiny which can allow us to create a web-based application to create dashboards
- Classic Modeling (Statistical Models) can be done to solve common data science problems such as
- Regression using Linear Regression
- Classification using Logistic Regression
- Segmentation using K-means
- Forecasting using ARIMA, ARIMAX, etc.
- Machine Learning models can be created using algorithms such as
- K Nearest Neighbor (KNN)
- Support Vector Machine (SVM)
- Naïve Bayes
- Decision Trees
- Ensemble Methods (Bagging, Boosting, Random Forest, Stacking aka Blending)
- Deep Learning models can be created using algorithms such as-
- ANN
- RNN
- CNN
- Auto Encoders
(2) Ease of Learning
R is easy to learn and this is something highly helpful for those who are from a non-computer background. As it is created by statisticians who were not technically computer programmers, the learning curve of R is relatively less steep as compared to other generic computer languages.
(3) Large Community
One of the biggest advantages of R is its CRAN-driven user community that keeps on upgrading R and keeping it up to date. This makes learning R programming fruitful as with the ever-changing environment where often language becomes obsolete, R has managed to stay relevant all these years.
(4) Business Friendly
R with its IDE R Studio provides servers and other services that make it a secure and reliable platform perfect for businesses. This is the reason that R even with being an open-source non-commercial suite, is accepted by a number of companies throughout the world.
(5) Compatibility
R can very well integrate with other platforms and frameworks. This includes the ease with which R can be run on Operating systems like macOS, Windows, Linux, etc, and can import data from multiple sources such as MS Excel, MySQL, Oracle, etc.
(6) Big Data
With the recent advancement in Big Data Analytics, a tool that has stood out to do this job has been R. It now has the required capabilities to connect to other Big Data-based technologies reviewing its importance in the dynamic world of Data Science.
Read: What does R training do to your data science skills
Python v/s R

The biggest competitor of R is Python. While they are similar as both of them are modular, dynamically typed, open-source languages with huge communities and are used in solving data science-based problems, there are significant differences also. While R is a language that was made for statistical computing, Python was created as a general-purpose language and it is because of libraries such as NumPy, pandas, and sci-kit learn that data science is possible in python.
If compared, R is a more non-standardized language which sometimes causes it to be slower than python. Python has more number IDEs whereas for R the only common IDE is R Studio. While integration is good in R, Python’s integration is even better which often makes it a tool for performing end-to-end projects. In the real world, the share of R is relatively less than python, however, in the field of academia startups, and research, R sometimes outshines python.
For a more detailed comparison, read our blog on Python vs. R vs. SAS
How To Learn R Programming Language

In order to learn R programming language, you can use multiple platforms. This includes academic courses on R common during bachelor’s or masters in economics, statistics, data science, and sometimes computer sciences. You can also learn R from online courses run by Data Science Institutions such as AnalytixLabs, Jigsaw, etc. Another great way to learn R is from books and blogs on R. However, the important thing is to concentrate on aspects of R that can help the user to learn R quickly and efficiently.
Read: Learning tip 101: Learn R Programming Language to stay relevant
These important aspects are as follows-
1. Understanding R Fundamentals
In order to learn about R, one must start with the fundamentals mentioned above. No matter how advanced you get into R, the fundamentals will support you throughout. Therefore, having a good knowledge of data types, structures, loops, classes, functions etc is important.
2. Exploring Important Packages
There are more than 15,000 packages in R, thus it becomes important to know which libraries to explore first to reach a decent lever in R as not all libraries are of equal importance. Some of the Common Packages / Libraries include
- System Libraries (Around 40+ libraries)
- utils (Essential utility work)
- stats (statistical computation)
- base (very basic functionalities)
- User Libraries (More than 15,000)
- Data Manipulation
- dplyr
- reshape2
- data.table
- Visualization
- plotly
- ggplot2
- Modeling (statistical as well as machine learning)
- caret
- h20.ai
- Data Manipulation
3. Implementing Documentation
One must learn how to read the help section of a function, explore the sample examples, understand the use of various arguments and implement them. This is the best way to expand on the knowledge of the functions.
4. Learning Statistics, Algorithms, and Business
No data science project works in a void. The knowledge of R needs to be complemented with knowledge of statistics (descriptive statistics, hypothesis testing, regression, etc), understanding of the various machine and deep learning algorithms and a good knowledge of how various business domains function and the issues they face. This helps in converting the programming prowess into providing a viable business solution.
5. Create Projects
Lastly, one must create projects. If datasets are not provided to you by your company or client then you must take publicly available datasets pertaining to different domains and apply all the knowledge of Data Science – Data importing, manipulation, mining, visualization, modeling, etc in R. This is the best way to gain confidence regarding the tool you are using.
Thus, the question of how to learn R programming language is a complex one as one needs to take care of multiple aspects of this language.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is an R Programming Language used for?
R programming language is used for data mining, visualization, statistical modeling, and creating predictive models using Machine Learning and Deep Learning algorithms.
Q2. Is it hard to learn R?
The R programming language does have a steep learning curve, however, if one pays attention to its fundamentals and learns how to go through the function’s documentation, it can be easy to learn. Also, if compared to other traditional languages such as C, C++, Java etc, it is extremely easy.

Q3. Is R Language in Demand?
As of 2022, most of the fortune 500 companies use R for solving their data analytics-based problems. Also, among the most popular data science languages, it is considered among the top 3. Also, especially in start-ups and research, knowledge of R is in demand. Here’s a quick overview of how your career will shape after you complete an R training program.
Conclusion
There are a number of tools that can help data science aspirants in implementing their knowledge, however, R stands out. It is because it is a unique language in the sense that it’s not a conventional programming language and is custom made for solving statistical and by extension data science-based problems. With the rapid adoption of data science across the globe, the demand for R is at an all-time high. Thus, along with other tools, one must have a decent knowledge of R even if it’s not their primary tool. Going forward, the reader must start with reading and doing some research on the basics of R mentioned before and expand on the knowledge of R gained from this article.







