Cybersecurity is paramount in our digitized world, where daily life relies heavily on information exchange. As technology advances, so do the threats of cybercrimes, elevating the importance of cybersecurity and robust measures to safeguard individuals, businesses, and governments.
According to the Cyber Threat Defense Report 2022, 85% of organizations have been successfully attacked by cybercriminals.
Over the past decade, the world has rapidly shifted towards digitization, with daily utilities now accessible online through e-commerce and various services. However, this convenience has a downside, as the increasing exchange of sensitive information makes individuals, businesses, and governments vulnerable to cybercrimes during transit and storage. The interconnectedness of devices and systems further amplifies these risks, making cybersecurity a critical concern in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Cyber Security aims to protect this data from theft and damage. Therefore, cyber security has gained massive importance to protect this information. Organizations and individuals must protect their data and systems from attack.
In this article, let us look at the importance of cybersecurity. Understand cyber security, the need for cyber security, and the rising scope for cyber security professionals.
What is Cyber Security?
Cybersecurity safeguards electronic systems from threats such as information theft and damage, as individuals, companies, and governments face risks from hackers seeking unauthorized access to data centers and digital systems.
With the increasing dependence on technology for convenience, including instant information access, on-demand services, entertainment, and smart automation, Cybersecurity is crucial in securing individuals and organizations utilizing these services.
Companies use it to protect against data breaches, ransomware attacks, and financial losses, whereas individuals use it against phishing schemes, spam, identity theft, and data breaches.
Cybersecurity is an umbrella term encompassing protection against all forms of cybercrime. Organizations enlist specialized professionals such as Cyber Security Analysts, Cyber Security Consultants, Vulnerability Analysts, Penetration Testers, and Cyber Security Managers to ensure effective security and prevent cyberattacks.
Global Approach to Cybersecurity
Governments across the globe are issuing recommendations and guidelines to protect individuals and organizations from cybercrime. Leading organizations are embracing API security and increasing the security budget to hire better-skilled people to protect cyberspace. According to global data, 64% of organizations have implemented API security. Other organizations are planning to implement Zero-Trust Network Access (ZTNA), and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE)
Need for Cyber Security
The importance of Cybersecurity can be seen as vital worldwide to protect against global damages. Organizations such as businesses, governments, and financial institutions are all interconnected to maintain the global economy. A severe cyber attack on any institute could damage our global economy and compromise sensitive data. Therefore, a globally collaborative cybersecurity approach is needed.
The cybersecurity global market size is anticipated to rise at a CAGR of 8.9% from USD 173.5 billion in 2022 to an estimated 266.2 billion USD by 2027. Therefore, cybersecurity is gaining momentum to ensure that important global infrastructure systems do not collapse. It is also essential for the continuity of financial institutions like banks and businesses. Hence, the importance of cybersecurity is also ever-increasing with technological advancement.
There are many reasons why cyber security is so important, like-
- The cost of dealing with a cyber attack is high- A single incident can cost a company millions of dollars in damage to its reputation, lost productivity, and recovery costs.
- Sensitive data can be compromised in a cyber attack- Breach of sensitive data can harm an individual. It allows criminals to commit fraud or other crimes.
- Profound impact on critical infrastructure- Cyberattacks can bring down critical IT infrastructure alongside impacting power grids or financial systems.
Types of Cyber Threats
Common types of cyber threats are:
- Cyberterrorism – Cyberterrorism is a cyber threat that is politically motivated to cause mass disruption among people and harm governments.
- Malware – Malware attack includes using ransomware, spyware, viruses, and worms to attack security. Various sophisticated techniques are developed to bypass and overcome security by installing harmful viruses and encrypting data.
- Trojans – Trojans are covert attacks on the system that is done by establishing a backdoor to allow access to the data. It tricks the victim into opening a harmless file and attaching itself to the system.
- Botnets – Botnets are a part of the system that attacks and remotely controls the affected system. These are highly coordinated attacks done to harm large organizations.
- Adware – Adware is a type of malware spread from advertising-supported software. The virus gets installed, which then bombards the victim with unwanted advertisements.
- Phishing – Phishing attacks often trick the victim using email or text. They ask for personal information like bank and social security numbers. They may even trick victims into installing apps containing malware.
- DoS – DoS stands for Denial of Service. It is an attack that overloads the network, making it incapable of fulfilling the victim’s request.
Types of Cybersecurity
There are many types of cybersecurity, and each offers its own unique set of benefits and features. Here are the most popular types of cybersecurity:
-
Critical Infrastructure Security:
Critical infrastructure security is related to critical cyber threats targeting an organization’s energy, transportation, financial services, healthcare, telecommunications, and other vital systems. These threats could potentially devastate public safety and even national security. Various nations have set protocols like the Critical Infrastructure Protection by the American government and the European Programme for Critical Infrastructure Protection to safeguard countries against collective threats.
An instance occurred in 2013 when Iranian hackers breached New York’s Bowman Avenue Dam. They gained control of the floodgates, dams, and port systems, but little damage was reported.
-
Application Security:
Application security helps to prevent various malware that attacks the apps and the devices hosting them. It includes identifying and addressing vulnerabilities in application code, architecture, and configurations. It is critical to prevent access to sensitive personal information.
Amazon suffered and mitigated a major Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack in February 2020. The 2.3 Tbps (Terabits per second) DDoS attack is considered to be the largest ever.
-
Network Security:
Network security prevents any attack that happens over networks. It includes measures to secure network infrastructure, prevent data breaches, and protect against denial of service attacks. Most of these security systems are custom-designed to identify and block cyberattacks.

In 2017, more than 300,000 computers in 150 countries were attacked by the WannaCry ransomware attack that caused damages of billions of dollars.
-
Cloud Security:
Cloud security is the process of protecting cloud-based applications and data from cyber-attacks. It includes measures to secure cloud infrastructure, prevent data breaches, and protect against denial of service attacks.
A notable incident of the cloud security breach was the data scraping breach of LinkedIn in 2021. Around 700 million LinkedIn profiles were hacked, and the scraped public data was posted on a dark web forum.
-
Zero Trust Solutions:
The Zero Trust security model protects the organization’s data by building a single focused perimeter firewall. It also monitors threats that are target-specific and uses security to counter them. The model assumes all users are untrustworthy until proven otherwise. It includes measures to authenticate and authorize users, encrypt data and limit access to systems and data.
An untraceable large-scale ransomware attack was reported in 2021. Known as Microsoft Exchange Remote Code Execution Attack, it affected government and private organizations.
-
Endpoint Security:
The endpoint security model secures devices by using preventive methods to secure endpoint devices, prevent data breaches, and protect against malware. It includes the use of anti-phishing and anti-ransomware technologies. These are also beneficial to detect any anomalies if any breach takes place.
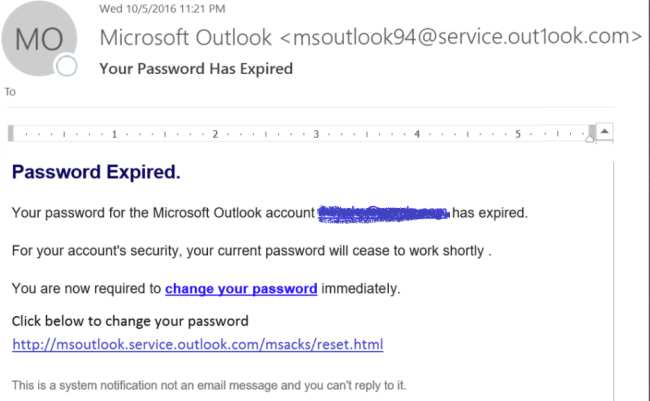
Phishing is not the newest yet most common form of cyberattack. The above example shows how scammers take advantage of urgency and panic. They use confusing text to compel end-users to click on a link and then share sensitive information.
-
Mobile Security:
Mobile security is protecting mobile devices from cyber attacks. It includes measures to secure mobile devices, prevent data breaches, and protect against malware.
Mobile phone virus scams, One-ring scams, SMS phishing (Smishing), and Voice mail scams (Vishing) are commonly reported mobile security breaches.
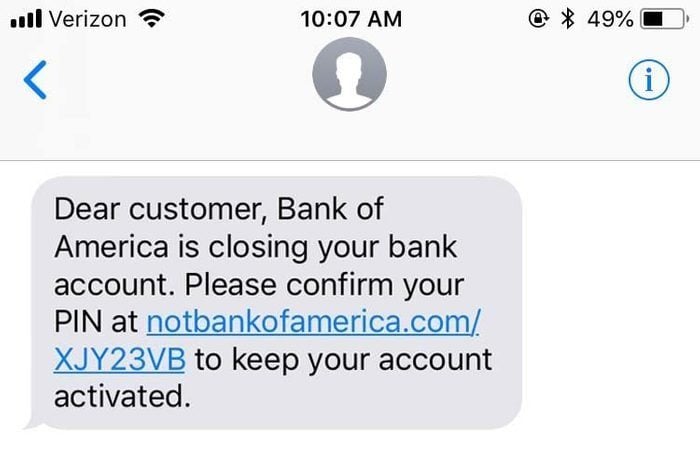 The above example clearly shows why you must not click any link without verifying it. Such SMS messages are drafted carefully by scammers to induce panic in the reader’s mind.
The above example clearly shows why you must not click any link without verifying it. Such SMS messages are drafted carefully by scammers to induce panic in the reader’s mind.
-
Industrial Control Systems Security:
Industrial control systems security protects industrial control systems from cyber-attacks. It includes measures to secure industrial control systems, prevent data breaches, and protect against denial of service attacks.
Colonial Pipeline Inc. was targeted by hackers in May 2021. It led to an acute fuel shortage in the US, and the company had to pay the hackers a huge sum of USD 4.4 million to regain control.
-
Internet of Things security:
Internet of Things (IoT) security protects Internet-connected devices from cyber attacks. It includes measures to secure devices, prevent data breaches, and protect against malware.
The most damaging DDoS attack ever, the Mirai Botnet, was launched on service provider Dyn in 2016. The IoT botnet searched for vulnerable devices on the Internet, such as digital cameras and DVR players, and infected them with the Mirai malware.
-
Cyber warfare:
Cyber warfare is using technology to conduct war in cyberspace. It includes offensive and defensive measures to disrupt enemy operations, protect friendly operations, and win battles.
Iranian nuclear program was reportedly attacked by the Stuxnet Virus. The malware targeted supervisory control systems disabling the country’s nuclear weapon manufacturing setup.
Why Cyber Security is Important?
The importance of Cybersecurity is on the rise due to the increase in technology reliance. The pandemic has made people more dependent on technology. It has also made digital adoption crucial for important organizations like banks, hospitals, and government offices.
As these organizations increasingly use the internet for everyday tasks, they tend to gather and process much user data. Hence, all the information collected by these organizations is stored online, which increases the risk of data leak and theft.
Criminals target these organizations to get access to information through unethical methods. They then use it for malicious activities like blackmailing, asking for ransom, extortion, selling bulk data, cyber stalking, etc.
The effect of cyberattacks could also be seen globally if a government or a social security system is hacked. Thus, having a great cybersecurity protocol at all levels is very important.
Benefits of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity holds paramount significance for businesses, irrespective of their size. Safeguarding data and systems not only mitigates the risk of cyber-attacks but also diminishes the impact of any potential breaches.
Implementing cybersecurity measures offers numerous advantages, such as:
- Protects against external threats such as malware, remote cyber attacks, Denial of service, trojan installation, and Zero-day exploits.
- Safeguards against internal threats due to human errors. Advanced technologies help to detect and automatically respond to errors. These internal threats could be prevented by monitoring and managing the human factor in organizations.
- Improving firewalls, taking backups, and preventing malware help secure an organization’s operations.
- Having cyber security in place helps the organization to maintain the trust and reputation among the clientele.
- Cost-effectively ensures organizational data security, preventing instances of falling victim to a cyber attack. Many hackers ask for an enormous ransom, hindering an organization’s operations.
Cyber Security Challenges
The cybersecurity landscape has evolved dramatically in recent years, with a surge in cyber-attacks and data breaches. This has led to a need for more sophisticated cybersecurity solutions that can protect businesses and individuals from these threats.
Several challenges must be addressed to improve an organization’s or individual’s cybersecurity. These include:
- Sophisticated Attacks: Cyber Security is challenged due to modern, sophisticated attacks done by criminals. These are not detected with the traditional approach but require a more concise investigation to identify and rectify the threat. They often require specific solutions, making it difficult to make unified policies as each attack differs.
- Complex Environments: An organization’s network’s complex nature makes enforcing strict security measures difficult. Monitoring the network also becomes difficult due to an organization’s infrastructure. Organizations are divided into hierarchies with multiple access points to data, making it difficult to pinpoint the exact vulnerabilities.
- Heterogeneous Endpoints: Many devices are connected to the organization as people bring them to work. This opens the network to many security risks and hence becomes a challenge. These connected devices could contain harmful files, resulting in an unknown data breach.
- Rise of Remote Work: Due to the rise of remote work culture during the pandemic, people use their devices. This makes cyber security challenging to monitor and enforce policies on various devices and could lead to a potential risk of leaking sensitive information.
Also read: How India is Handling Challenges of Cyber Security
What does cyber security protect?
Cybersecurity protects all types of data available in the digital world from those with malicious intent. The data could be personal information, health information, business information, government data, process workflows, and protocol data.
Cybersecurity protects the data from theft and loss due to ransomware. It protects people by making them aware and ensuring compliance with data security measures, such as using two-factor authentication, strong passwords, backing up data, VPNs, and reputable antivirus software. Protecting systems involves employing security tools like firewalls, DNS filtering, malware protection, and adhering to the principle of least privilege.
Cyber Security Best Practices
While there’s no foolproof solution in cybersecurity, businesses can enhance their protection by adopting several best practices. Here are a few recommendations:
-
Regular training and awareness sessions
Many security breaches take place due to unintentional human error. Even a great cyber security strategy will not be able to compensate for the damage done internally. Hence, an organization should invest in educating employees and spreading awareness of the best cyber security policies. These can be done by conducting seminars, online courses, and workshops.
-
Risk assessment and security review
An organization should conduct risk assessments and security reviews to protect the organization from cyber threats. It helps identify potential risks and vulnerabilities and implement controls to mitigate them. Risk assessments are done to ensure the organization’s valuable resources are secured. Security reviews should be conducted regularly to ensure no breach in the system.
-
Vulnerability management
All the software and systems used should be regularly monitored and kept up-to-date to avoid any vulnerabilities. Keeping up with vulnerabilities in your organization’s systems and applications is critical. Timely deployment of security updates and patches is crucial for maintaining a robust cybersecurity posture. Penetrations test and feedback loop should help to manage vulnerabilities in the system.
-
Principle of Least Privilege
Principle of least privilege (PoLP) is a security best practice stipulating that users should only have the level of access needed to perform their job duties. This helps limit the damage a malicious user or insider threat can cause. All the accounts should have two-factor authentication to ensure the system’s protection.
-
Ensure secure password storage and policies
The organization should have a strong password manager and generator application to protect the data. They should be regularly changed to safeguard the system from getting compromised.
What is a Cyber Security Course?
Cybersecurity courses equip students with essential analytical and technical skills to protect data, individuals, and organizations from cyber threats. These programs cover ethical hacking, cryptography, firewalls, intrusion detection, vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, network defense, and malware protection.
Cybersecurity courses are offered at both undergraduate and graduate levels. These courses prepare individuals to formulate policies and actively monitor systems against malicious intent. There is a growing demand and handsome salaries for qualified cybersecurity professionals as more and more businesses and organizations store sensitive information electronically.
The Cyber Workforce Report of The International Information System Security Certification Consortium found that the cybersecurity workforce needs to elevate by 65% to protect an organization’s assets effectively.
The demand for cybersecurity experts will increase by 28% by 2026, as the US Bureau of Labour Statistics predicted, making it a lucrative career option. A cyber security course can give students and professionals the skills and knowledge they need to enter this exciting field.
Also read: Roadmap to Becoming a Cyber Security Expert in India in 2023
Frequently Asked Questions:
1. What are 7 types of cyber security?
There are seven types of Cybersecurity depending on the use case. They are Critical Infrastructure Security, Application Security, Network Security, Cloud Security, Zero Trust Solutions, Endpoint Security, and Internet of Things security.
Identifying and blocking attacks across the network, Network Security safeguards the cloud from data breaches, as it has the storage of a substantial portion of data. The endpoint Security model secures devices using preventive methods like anti-phishing and anti-ransomware technologies.
Trained specialists address threats to networks, cloud-based systems, and mobile applications, recommending seven types of cybersecurity tailored to the specific cyberattacks devices face.
2. What is a cyber security example?
Various examples of cyber security incidents have continuously risen due to the pandemic. Phishing, downloaders, and ransomware are the most used methods to cause breaches.
More than 60% of social engineering-related incidents are due to phishing, as the 2022 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report reported. Around mid-July 2020, Twitter was a victim of a large spear-phishing attack.
On the night of July 22, two Luxembourg-based companies, Creos and Enovos, were attacked by a BlackCat ransomware attack, which resulted in the loss of 150 GB of sensitive data. There are many such examples of data breaches. Hence, increasing measures and spreading awareness around cyber security is important.
3. Who uses cyber security?
Businesses, organizations, and individuals use cyber security to protect themselves from online threats. Businesses protect their networks and data from attacks, while organizations use it to secure their communications and systems. Individuals can use cyber security to protect their personal information and devices from criminals.
Anyone(individual or organization) using online services connected to the internet should generally employ cybersecurity measures. Cybersecurity protects all types of data available and the people connected online.
Cyber security measures such as two-factor authentication, strong passwords, backing up data, using VPN, and using reputed antivirus software protect individuals and teams connected online. Large corporations and organizations must follow different security protocols and strategies to safeguard their assets and data.








